Alzheimer’s disease and dementia are formidable challenges that affect millions of individuals worldwide, profoundly impacting their cognitive abilities and quality of life. As the search for effective treatments continues, medical marijuana has emerged as a topic of interest and exploration. With its potential therapeutic properties, medical marijuana holds the promise of providing relief for those affected by Alzheimer’s and dementia. In this blog, we will delve into the current state of knowledge surrounding medical marijuana as a treatment option for these neurodegenerative conditions. By examining the existing research and understanding the complexities of this alternative approach, we aim to shed light on what we know so far and the potential it holds for individuals facing the devastating effects of Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Understanding Alzheimer’s and Dementia:
Alzheimer’s disease and dementia are both neurological conditions that primarily affect memory, cognitive function, and behavior.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterized by progressive memory loss, difficulty with language and communication, confusion, and changes in personality and behavior. It is a degenerative brain disorder that results in the gradual deterioration of brain cells, leading to a decline in cognitive abilities.
Dementia, on the other hand, is an umbrella term that encompasses a range of conditions characterized by cognitive impairment severe enough to interfere with daily functioning. While Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent cause of dementia, there are other types such as vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and mixed dementia. Each type has its unique set of symptoms and underlying causes, but they all share the common characteristic of cognitive decline.
Both Alzheimer’s disease and dementia have a significant impact on individuals’ ability to remember, think clearly, make decisions, and carry out daily activities. The progression of these conditions can be challenging for individuals affected and their families, requiring specialized care and support. Understanding these disorders and exploring potential treatment options is crucial in order to enhance the quality of life for those living with Alzheimer’s and dementia.
The Endocannabinoid System and its Role in the Brain:
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in the brain and throughout the body. It is composed of endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes that work together to maintain balance and homeostasis.
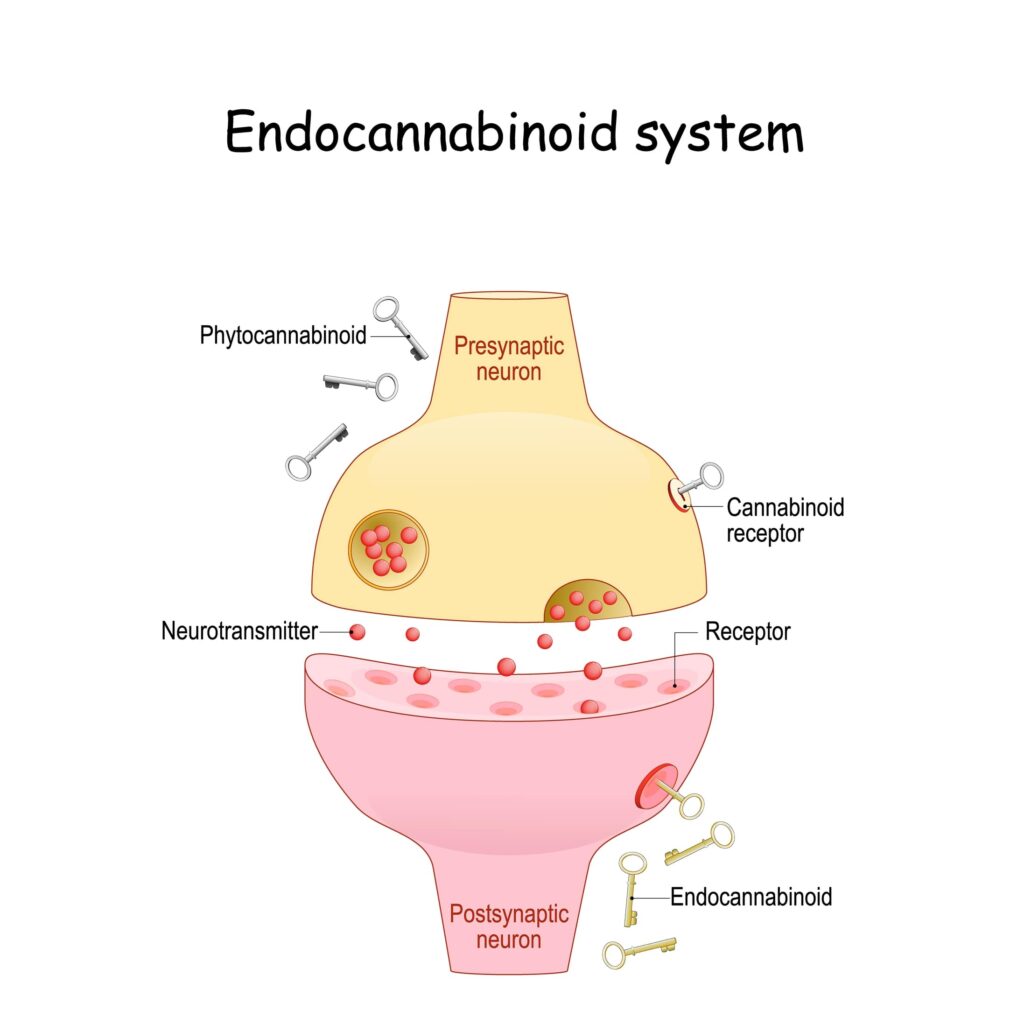
In the brain, the ECS is involved in several essential functions, including:
- Neurotransmission: The ECS modulates the release of neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons. It helps regulate the balance of excitatory and inhibitory signals, influencing processes such as learning, memory, mood, and cognition.
- Neuroprotection: The ECS has been found to have neuroprotective properties, meaning it helps protect brain cells from damage and promotes their survival. It plays a role in reducing neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity, all of which can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases.
- Synaptic Plasticity: Synaptic plasticity refers to the ability of synapses (connections between neurons) to strengthen or weaken over time, influencing learning and memory. The ECS is involved in modulating synaptic plasticity, affecting the formation and consolidation of memories.
- Regulation of Stress and Anxiety: The ECS is closely linked to the regulation of stress responses and anxiety. It interacts with regions of the brain involved in emotional processing, helping to modulate stress and anxiety-related behaviors.
The endocannabinoids produced by our body, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), bind to cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB1 and CB2 receptors, found throughout the brain and nervous system. When endocannabinoids bind to these receptors, they trigger a cascade of signaling events that regulate various physiological processes.
Understanding the role of the endocannabinoid system in the brain is essential in exploring the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids, including those found in medical marijuana, for neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s and dementia. By targeting the ECS, researchers aim to harness its potential to modulate brain function and provide therapeutic benefits.
The Potential Benefits of Medical Marijuana for Alzheimer’s and Dementia:
Medical marijuana has shown potential benefits for individuals with Alzheimer’s and dementia, although more research is needed to fully understand its effects. Some of the potential benefits that have been observed or theorized include:

- Symptom Management: Medical marijuana may help alleviate various symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s and dementia. It has been reported to reduce agitation, anxiety, and aggression, which can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with these conditions. Additionally, it may help manage sleep disturbances, appetite loss, and depression commonly experienced by patients.
- Cognitive Enhancement: There is preliminary evidence suggesting that certain cannabinoids found in medical marijuana, such as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), may have cognitive-enhancing effects. These compounds have been shown to modulate neurotransmitter systems involved in memory and cognition, potentially improving cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s and dementia. However, more research is needed to establish the effectiveness and safety of medical marijuana for cognitive enhancement.
- Neuroprotective Properties: Some studies suggest that cannabinoids found in medical marijuana possess neuroprotective properties, meaning they may help protect brain cells from damage and promote their survival. This could potentially slow down the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity in the brain.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is believed to play a role in the progression of Alzheimer’s and dementia. Medical marijuana has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, potentially reducing inflammation in the brain and mitigating the damage caused by neuroinflammation.
- Appetite Stimulation and Weight Management: Loss of appetite and unintended weight loss are common issues in individuals with Alzheimer’s and dementia. Medical marijuana, particularly strains containing THC, may stimulate appetite and help manage weight loss by activating cannabinoid receptors involved in regulating hunger and satiety.
It’s important to note that individual responses to medical marijuana can vary, and its effects may differ based on factors such as dosage, strain, and the specific composition of cannabinoids and terpenes. Additionally, legal and regulatory considerations, as well as potential side effects and drug interactions, should be carefully evaluated before considering medical marijuana as a treatment option. Consulting with healthcare professionals experienced in cannabinoid-based therapies is crucial for personalized and informed decision-making.
Challenges and Considerations:
While medical marijuana holds potential as a treatment option for Alzheimer’s and dementia, there are several challenges and considerations that need to be taken into account:
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations: The legal status of medical marijuana varies across countries and even within different regions or states. Regulations may limit access, pose restrictions on the types and forms of medical marijuana available, and require specific qualifications or prescriptions. Understanding the legal framework and complying with regulations is essential for individuals, caregivers, and healthcare providers.
- Lack of Standardization and Quality Control: The composition of medical marijuana products can vary significantly, including the concentration of cannabinoids and other compounds. Inconsistent formulations and lack of standardized dosing present challenges in achieving consistent therapeutic effects. Ensuring quality control, proper labeling, and standardized formulations are necessary to enhance safety and efficacy.
- Potential Side Effects and Risks: Like any medication, medical marijuana can have side effects. These can include drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, impaired coordination, and changes in mood or cognition. Additionally, THC, the psychoactive compound in marijuana, may cause confusion, anxiety, or paranoia, which can be particularly concerning for individuals with cognitive impairments. Understanding the potential risks and monitoring for adverse effects is crucial.
- Drug Interactions: Medical marijuana can interact with other medications, potentially affecting their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals to evaluate potential drug interactions and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Lack of Conclusive Evidence: While there is a growing body of research on medical marijuana for Alzheimer’s and dementia, the evidence is not yet conclusive. Many studies have limitations in sample size, study design, or duration. Further research, including large-scale clinical trials, is needed to establish the long-term safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing strategies for medical marijuana in this context.
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Each person with Alzheimer’s or dementia is unique, and their response to medical marijuana may vary. Developing individualized treatment plans that consider factors such as medical history, overall health, cognitive function, and potential risks is crucial. Close monitoring and regular evaluations are necessary to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make any necessary adjustments.
- Caregiver Support and Education: Medical marijuana use for Alzheimer’s and dementia requires caregiver support and education. Caregivers need to understand the potential benefits, risks, and administration methods to ensure safe and effective use. Additionally, caregiver well-being and access to support systems should be prioritized.
Navigating these challenges and considerations requires collaboration among healthcare providers, patients, caregivers, and regulatory authorities. Open communication, research advancements, and continued education can help address these challenges and improve the potential for medical marijuana as a treatment option for Alzheimer’s and dementia.
In Conclusion:
In conclusion, medical marijuana holds promise as a potential treatment option for individuals living with Alzheimer’s and dementia. While research suggests potential benefits such as symptom management, cognitive enhancement, neuroprotection, anti-inflammatory effects, and appetite stimulation, more rigorous studies are needed to establish its efficacy, safety, and optimal usage. Legal and regulatory considerations, lack of standardization, potential side effects, drug interactions, and the need for individualized treatment plans pose challenges that must be carefully addressed. By navigating these complexities and continuing to advance research, we can gain a better understanding of the role medical marijuana can play in improving the lives of those affected by Alzheimer’s and dementia. It is essential to approach medical marijuana use in this context with caution, informed decision-making, and the guidance of healthcare professionals experienced in cannabinoid-based therapies. With further exploration, medical marijuana may provide valuable contributions to comprehensive care strategies for Alzheimer’s and dementia, offering hope for enhanced quality of life and better management of these challenging conditions.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.





