Did you know that your nervous system is actually made up of two systems known as the central and peripheral nervous systems? Your central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord, while your peripheral nervous system is made up of all the nerves outside your brain and spinal cord. This blog post will discuss these two systems as well as some neurological disorders that can affect each system. An important thing to note is that neurological disorders can affect one or both systems at once!
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) includes your brain, spinal cord, and neurons.
Brain
The brain is composed of the brainstem, cerebellum, and cerebral hemispheres.
- Brainstem: connects the brain to the spinal cord
- Cerebellum: part of the hindbrain that is located under the cerebrum near the brainstem. The cerebellum is responsible for voluntary movements, motor function, balance and posture, vision, motor learning, and mental function.
- Cerebrum: largest part of the brain and is in charge of thought, memory, speech, and voluntary behaviors. The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres, which are then divided into four lobes known as the frontal, occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is connected to the brain through the brain stem and then extends down through the spinal canal. The entire spinal cord is encased in spinal bones known as vertebra. Movements known as reflexes are controlled by the spinal cord.
Neurons
Neurons are another name for nerve cells. They are found all over the body, however most neurons are found within the brain, specifically the cerebellum.
The CNS receives sensory information from the body and then initiates a response. To protect the CNS and promote proper function, it is covered in a tissue known as the meninges and submerged in cerebrospinal fluid.
Central Nervous System Disorders
Now that we know a little more about the components and function of the CNS, let’s look at some neurological disorders that can affect the CNS:
Encephalitis/meningitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain, while meningitis is inflammation of the meninge membrane around the brain and spinal cord. Both conditions can occur as a result of a viral infection.
Stroke
A stroke, also known as cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is suddenly interrupted or when a blood vessel in the brain gets damaged causing bleeding in the surrounding brain tissue. Brain cells die when they no longer receive oxygen and nutrients from the blood or there is sudden bleeding into or around the brain. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease in which the myelin sheath which is the covering of the brain and spinal cord gets damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to communicate, resulting in a wide range of signs and symptoms including abnormal sensation, muscle weakness, mental and sometimes psychiatric problems.
Neurodegenerative Disorders
Neurodegenerative disorders are characterized by the progressive death of neurons that cause problems with movement (ataxias) or mental functioning (dementias). Some common neurodegenerative disorders include Alzheimer’s, ALS, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease.
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system is made up of all the nerves that connect your brain to the rest of your body, such as organs, limbs, and skin. Basically, any nerve outside of your brain or spinal cord is part of your peripheral nervous system. The PNS connects your brain and spinal cord in order to allow information to be sent and received between the brain and other parts of the body.
Within the peripheral nervous system, there are two components:
Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system is in charge of voluntary movements, which are your conscious actions. For example, when you decide to pick up a cup of water it is the somatic nervous system that tells your hand and arm muscles what to do so you can accomplish this task. The somatic nervous system contains both motor neurons which are responsible for carrying nerve impulses to the muscles, as well as sensory neurons, which carry sensory information to the brain and spinal cord.
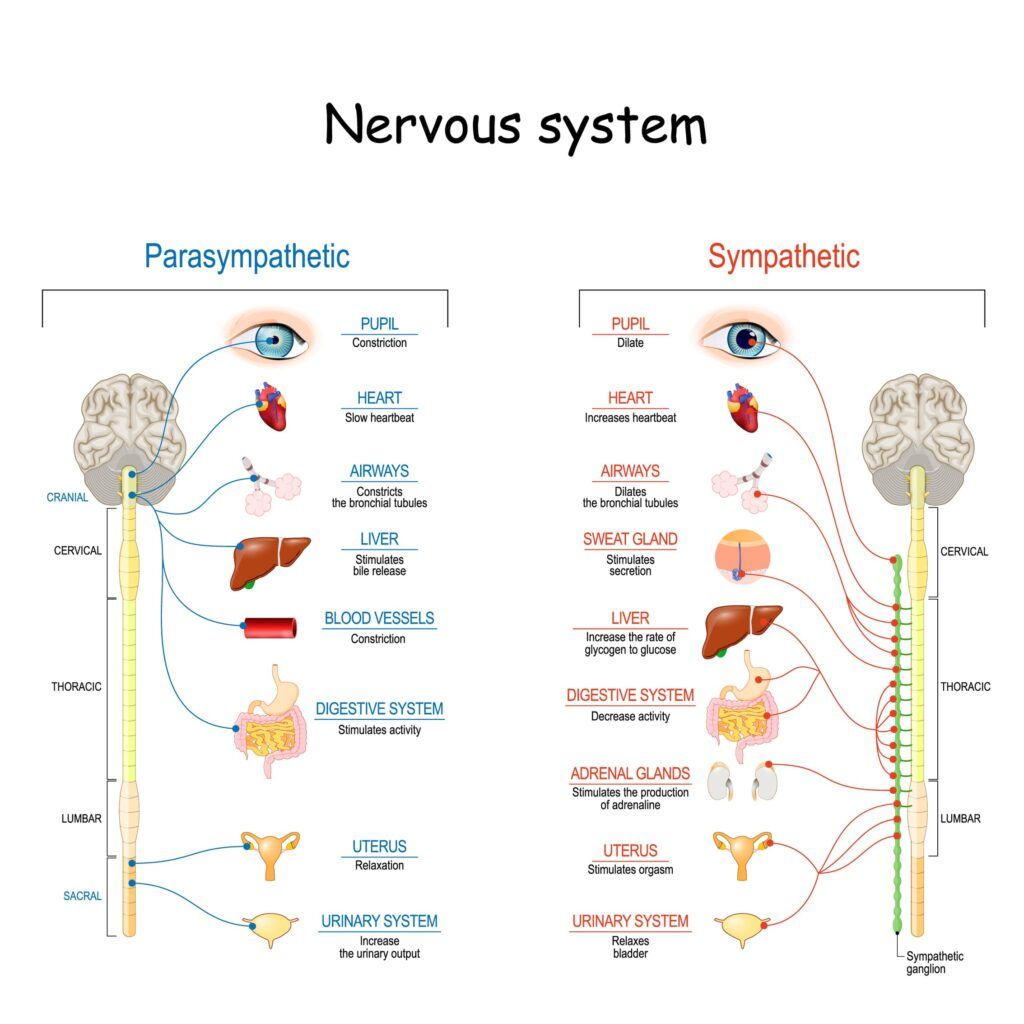
Autonomic Nervous System
For involuntary functions such as breathing, digestion, and blood pressure regulation you need the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is divided into two branches known as the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): The SNS works to prepare your body for fight or flight situations by increasing heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose. These are all bodily systems that need to be increased when an individual is under stress or perceives a threat in order for the body to have enough energy to fight or flee from danger.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): The PNS opposes the SNS by promoting the opposite bodily functions. This is when the body needs to relax, digest food in order to produce energy, and lower heart rate in cases of emergencies where an individual does not need high amounts of energy for fight or flight situations.
Peripheral Nervous System Disorders
There are also several disorders that can affect your peripheral nervous system. These include:
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
A type of autoimmune disorder where the body attacks nerve cells with your PNS. This causes muscle weakness, tingling, and sometimes paralysis. This disease is rare, however it can occur after a respiratory infection, viral infection, or bacterial infections.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy is the deterioration of neurons in your peripheral nervous system. This can be due to a variety of different reasons, however it is most commonly associated with diabetes and exposure to toxins such as heavy metals or chemicals. Symptoms include tingling sensations, pain, numbness, muscle weakness/fatigue, and/or loss of sensation.
Radiculopathies
Radiculopathy is a disease or injury of the spinal nerve roots that causes radicular pain, weakness, numbness, and/or tingling in the arms or legs. It can occur as a result of sports injuries, heavy lifting, bad posture, or diseases that cause the spine to degenerate.
To Sum It Up
- The CNS is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and neurons
- CNS disorders include stroke, multiple sclerosis, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s
- The PNS is composed of the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
- PNS disorders include Guillain-Barre Syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, and radiculopathy

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.




