Do you ever feel like your hands are numb? That tingling, “pins and needles” feeling that comes and goes without warning? You’re not alone. Many people experience numbness in their hands, for a variety of reasons. In this blog post, we will explore the six most common neurological causes of numbness in the hands and what to do if you experience this symptom. We will also explain when numbness in the hands could indicate an emergency. Finally, we will explain how a neurologist diagnoses and treats numbness in the hands.
What does numbness feel like?
Numbness in the hands is often described as a tingling, “pins and needles” feeling. This sensation can come and go without warning and may be accompanied by other symptoms like weakness, pain, or fatigue. Numbness in the hands can be a sign of an underlying neurological condition. If you experience numbness in your hands, it is important to seek medical attention, as some causes of numbness can be life-threatening.
In some cases, you may need to seek emergency medical attention, especially if numbness in the hands is accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Weakness
- Paralysis
- Loss of balance
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Vision changes
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Rash
- Numbness in other body parts
- Loss of bladder/bowel control
What are the six most common neurological causes of numbness in the hands?
There are many potential neurological causes of numbness in the hands. Here are six of the most common:
Stroke:
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. This can happen due to a clot or bleeding in the brain. Symptoms of a stroke typically come on suddenly and may include numbness in one hand, paralysis, weakness, difficulty speaking or swallowing, and vision changes. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as a stroke is a medical emergency and early treatment is essential to prevent long-term effects.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the median nerve in the wrist. The median nerve is responsible for feeling in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger. Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness and tingling in the hands, weakness, and pain. Carpal tunnel syndrome is typically diagnosed with a physical exam and nerve conduction study. Treatment options include splinting, physical therapy, and surgery.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome:
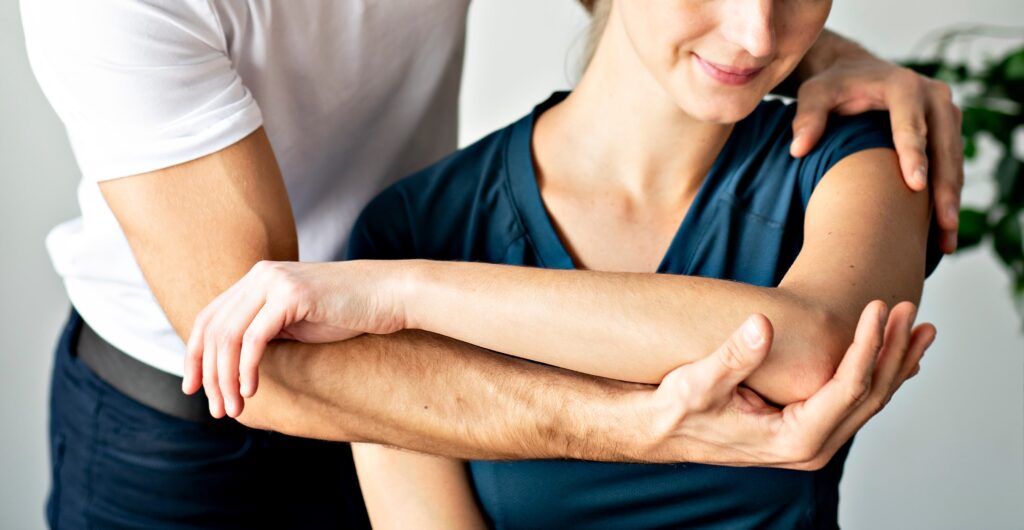

Cubital tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve in the elbow. The ulnar nerve runs from the neck all the way into the pinky finger. Symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome include numbness and tingling in the hands, weakness, and pain. In most cases, numbness tends to occur in the ring and pinky fingers, however pain and weakness may also be felt in the forearm. Cubital tunnel syndrome is typically diagnosed with a physical exam and nerve conduction study. Treatment options include splinting, physical therapy, and surgery.
Alcohol-Related Neuropathy:
Alcohol-related neuropathy is caused by damage to the nerves due to alcohol abuse. It generally occurs from drinking large amounts of alcohol, but it can also occur as a result of drinking with kidney or liver disease. Symptoms of alcohol-related neuropathy include numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet. It can also cause muscle spasms, problems with bladder control, and erectile dysfunction in males. Treatment options include decreasing alcohol intake.
Multiple Sclerosis:
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that attacks and damages the protective coating around the nerves. Symptoms of multiple sclerosis include numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, weakness, pain, fatigue, and vision changes. Oftentimes, numbness tends to affect one side of the body. Multiple sclerosis is typically diagnosed with a physical exam, MRI, and blood tests. There is no cure for multiple sclerosis, but treatments can help manage symptoms.
How is numbness in the hands diagnosed and treated by a neurologist?
A neurologist will first take a medical history and ask you about your symptoms, how long you have been experiencing symptoms, and whether the symptoms have progressed. They will then perform a physical exam, as well as a neurological exam to assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation.
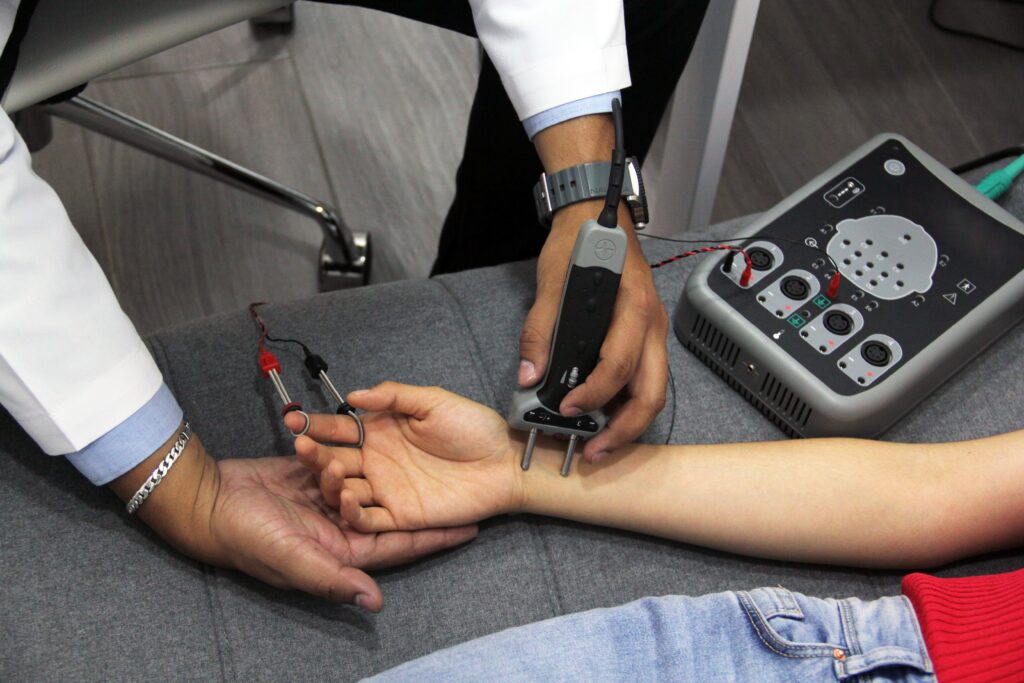
Based on your symptoms and the findings of the neurological exam, your doctor may also order tests, such as blood tests, MRI, or nerve conduction studies to further assess your condition. In some cases, multiple tests are needed to rule out certain conditions and narrow down the cause of your numbness.
Once a diagnosis has been made, then your neurologist will develop a treatment plan. Treatment for numbness in the hands will depend on the underlying cause, as well as the severity of your symptoms. In some cases, treatment may include physical therapy, medications, or surgery. Some conditions can be resolved with treatment, while others can only be managed. Overall, treatment for hand numbness is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of symptoms, hand numbness or otherwise.
In Conclusion
In this blog, we have discussed six possible reasons your hands may be numb. We have also briefly explained what each condition feels like, as well as other associated symptoms. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms we have mentioned, we recommend that you see a neurologist to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. As specialists in neurological conditions, neurologists have the experience and resources necessary to accurately diagnose and treat various causes of numbness in the hands.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.





