Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), often referred to as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a devastating neurodegenerative disorder that affects the motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. As the disease progresses, individuals with ALS experience a gradual loss of muscle control, leading to severe disability and, eventually, paralysis. Currently, there is no cure for ALS, and treatment options are limited. However, in recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential of medical marijuana as a complementary therapy for ALS. In this blog, we’ll explore the current state of research and the potential benefits of medical marijuana for ALS patients.
Understanding ALS
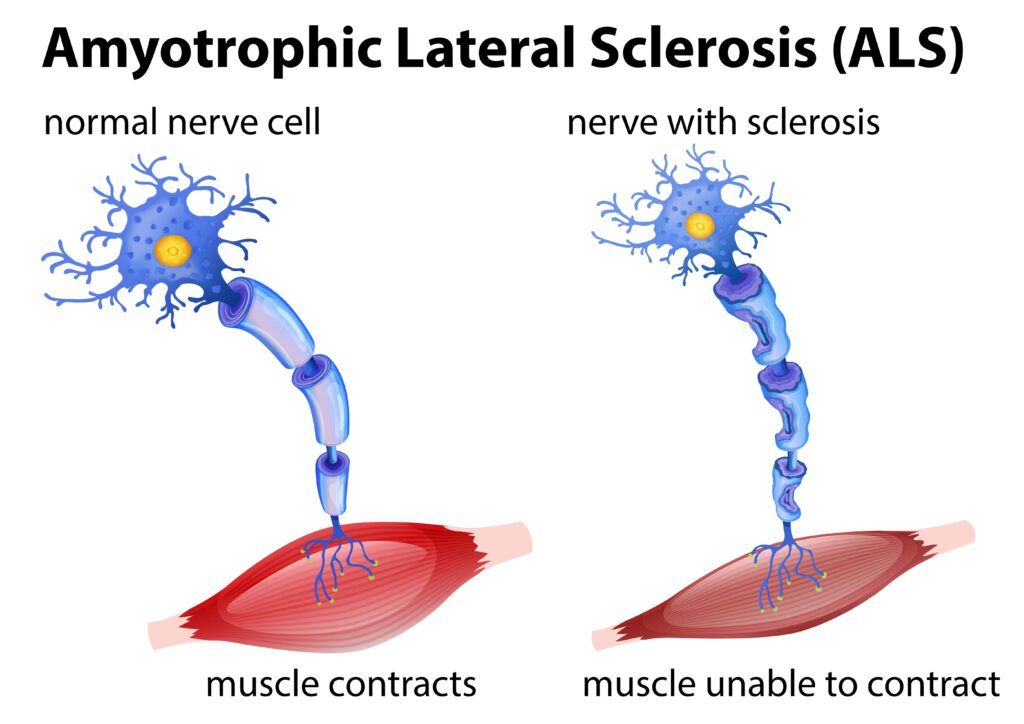
Before delving into the potential benefits of medical marijuana, it’s essential to grasp the underlying mechanisms of ALS. The disease primarily affects motor neurons, which are responsible for transmitting signals from the brain to the muscles, enabling voluntary muscle movement. As ALS progresses, motor neurons degenerate and die, leading to muscle weakness, twitching, and eventually paralysis.
The precise cause of ALS remains unclear, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to contribute to its development. There is currently no cure for ALS, and treatment options focus on managing symptoms, slowing the progression of the disease, and improving the quality of life for patients.
Conventional ALS Treatments
While there is no cure for ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis), several conventional treatments and therapies are available to help manage the symptoms, slow the disease’s progression, and improve the quality of life for individuals with ALS. These treatments are typically provided by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including neurologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and respiratory therapists. Here are some of the conventional treatments and therapies commonly used for ALS:
Riluzole (Rilutek):
Riluzole is an FDA-approved medication that can help slow the progression of ALS to some extent. It is believed to work by reducing the release of glutamate, a neurotransmitter that can be toxic to motor neurons when present in excessive amounts. While riluzole is not a cure, it may extend the time before a person with ALS requires ventilation support.
Edaravone (Radicava):
Edaravone is another FDA-approved medication for ALS. It is administered intravenously and is believed to have antioxidant properties that may help reduce oxidative stress and slow the progression of the disease. Like riluzole, edaravone is used to modestly slow functional decline in ALS.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining mobility and preventing muscle stiffness and contractures. Physical therapists work with ALS patients to develop exercise routines and techniques that can help maximize their physical function and independence.
Occupational Therapy:
Occupational therapists focus on helping ALS patients adapt to changes in their daily activities and environment. They provide guidance on assistive devices, adaptive techniques, and strategies to maintain independence in activities of daily living.
Speech Therapy:
Speech therapists assist individuals with ALS in managing speech and swallowing difficulties. They may recommend communication devices, exercises, and techniques to help patients communicate effectively and safely eat and drink.
Respiratory Therapy:
As ALS progresses, individuals may experience respiratory muscle weakness, leading to breathing difficulties. Respiratory therapists can provide non-invasive ventilation (NIV) and other respiratory support options to improve breathing and oxygenation.
Assistive Devices:
Various assistive devices, such as wheelchairs, mobility aids, communication devices, and home modifications, can enhance the quality of life and promote independence for ALS patients.
Nutritional Support:
Maintaining adequate nutrition is essential for ALS patients who may have difficulty swallowing and chewing. Dietitians can help create customized meal plans and recommend supplements or feeding tubes when necessary.
Psychological and Emotional Support:
ALS can be emotionally challenging for both patients and their caregivers. Support from mental health professionals and support groups can provide emotional and psychological support throughout the journey.
Palliative Care and Hospice:
As ALS is a progressive and ultimately fatal disease, palliative care and hospice services can provide comprehensive end-of-life care to manage pain, discomfort, and emotional distress while maximizing comfort and quality of life.
It’s important to note that while these treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life, they do not provide a cure for ALS. Researchers continue to explore potential therapies and interventions in the hope of finding more effective treatments for this devastating disease.
The Role of Medical Marijuana
Medical marijuana, also known as medical cannabis, refers to the use of cannabis or its chemical components for therapeutic purposes under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Cannabis contains over 100 different compounds, known as cannabinoids, with the two most well-known being delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
Researchers have been studying the potential benefits of medical marijuana for ALS patients, primarily due to its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and pain-relieving properties. Here are some ways in which medical marijuana may offer relief to individuals with ALS:
Pain Management:
ALS patients often experience chronic pain, muscle cramps, and spasms due to muscle weakness and degeneration. Cannabis contains compounds known as cannabinoids, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), which have analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. These cannabinoids may help reduce pain and muscle discomfort.

Appetite Stimulation:
Weight loss and malnutrition are common in ALS patients due to difficulty swallowing and reduced appetite. Medical marijuana can stimulate appetite, potentially improving nutrition.
Muscle Relaxation:
Muscle stiffness and spasticity are common symptoms of ALS. THC, in particular, has muscle relaxant properties that can help alleviate muscle tension and spasms, providing relief to some patients.
Anxiety and Depression:
An ALS diagnosis can be emotionally distressing, leading to symptoms of anxiety and depression. Some individuals have reported experiencing improved mood and reduced anxiety after using medical cannabis.
Sleep Quality:
Sleep disturbances are common in ALS patients, and medical cannabis may help improve sleep quality for some individuals, promoting better rest and overall well-being.
Neuroprotection:
There is emerging research suggesting that cannabinoids may have neuroprotective properties, potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like ALS. This is an area of ongoing investigation and not yet fully understood.
It’s important to note that while medical cannabis may provide relief for some ALS patients, it is not a cure for the disease, and its effectiveness can vary from person to person. Additionally, the use of medical cannabis should be approached cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, particularly due to potential side effects and legal considerations.
Research
Research on ALS and medical cannabis has garnered attention due to the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids in alleviating symptoms and possibly slowing the progression of this devastating neurodegenerative disease. While clinical studies in this field have been relatively limited, ongoing research has been exploring the use of medical cannabis, particularly cannabinoids like THC and CBD, in managing symptoms such as pain, muscle spasticity, and appetite loss in ALS patients. Additionally, preclinical studies have investigated the neuroprotective properties of cannabinoids and their impact on motor neuron function. Although the evidence is still evolving, the research holds promise in offering new insights into how medical cannabis may enhance the quality of life for ALS patients and potentially contribute to our understanding of the disease’s underlying mechanisms.
Conclusion
ALS remains a devastating and currently incurable disease that severely impacts the lives of those affected. While medical marijuana shows promise as a potential complementary therapy, more research is needed to establish its safety and efficacy for ALS patients. Patients considering medical marijuana should consult with a board-certified medical marijuna doctor to explore the potential benefits, risks, and legal considerations.
In the future, as research continues and regulations evolve, medical marijuana may become a valuable tool in the comprehensive care and support of ALS patients, offering relief from symptoms and improving their quality of life. Until then, ongoing scientific exploration and advocacy efforts are crucial to unlock the full potential of medical marijuana as a therapeutic option for ALS.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.




