Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment that many people are familiar with. However, did you know that it can also be used for medical purposes? In this blog post, we will discuss 5 ways your neurologist uses Botox to treat neurological conditions.
What is Botox?
Botox is a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It works by blocking nerve impulses to the muscles, which results in a temporary paralysis of the muscle. This makes it an effective treatment for a variety of medical conditions.
Ways Neurologists Use Botox
Botox for Migraine
Migraines are a common condition that can be debilitating. They are often characterized by severe headaches, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Botox has been found to be an effective treatment for people who have severe migraines lasting 15 days or more. It is thought to work by reducing the activity of the muscles that control the nerve endings involved in migraines. When injected into the neck and forehead, Botox blocks the nerve signals responsible for triggering migraines. However, Botox does not override migraine triggers.
One dose of Botox lasts for 10-12 weeks and has been found to reduce migraines by 50% with multiple treatments. Most people experience relief within 4-7 days of their treatment. However, it can take up to six months to notice maximum results.
Botox for Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm is a condition that causes involuntary muscle contractions in the eyelids. This can result in the eyes being forced shut and can be very painful.
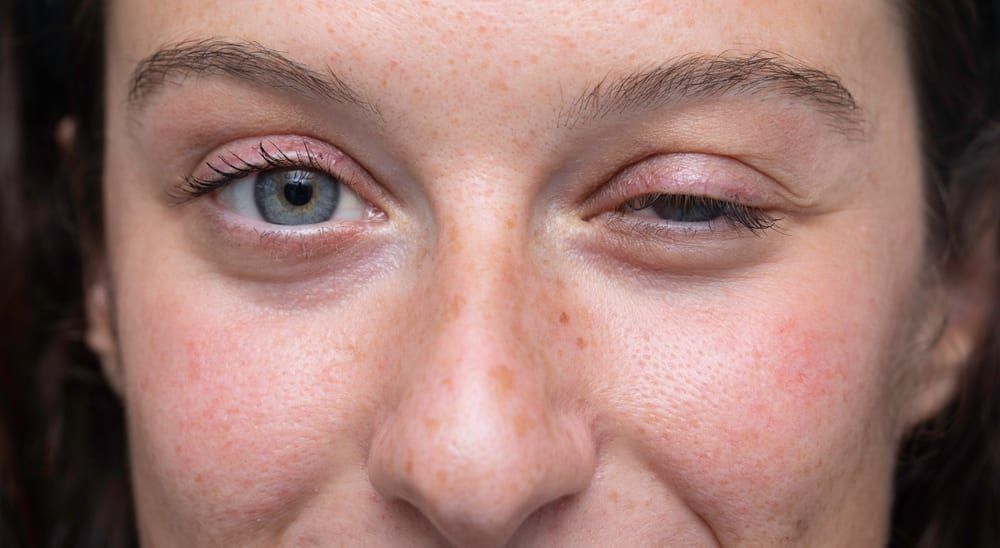
Botox is an effective treatment for blepharospasm because it relaxes the muscles that are causing the spasms. This can provide relief from the pain and allow the eyes to open. Botox can also reduce excessive blinking, light sensitivity, eye dilation, dry eyes, and eye irritation.
One dose of Botox lasts for 12 weeks, and multiple treatments have been found to be effective in managing blepharospasm symptoms. The injection is usually given in the upper eyelid muscles and only takes about 10-15 minutes. After Botox, patients may experience some minor discomfort and bruising around the eyes. However, they should also notice an improvement in their symptoms.
Botox for Spasticity
Spasticity is a condition that is characterized by muscle stiffness and spasms that prevents normal walking, movement, and speech. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, such as spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, and stroke.
Botox can be used to treat spasticity by relaxing the muscles. This can help to reduce the severity of spasms and improve range of motion. Not only that, but Botox can allow the nervous system to grow new muscle nerves to produce normal nerve communication. Overall, Botox gradually relieves pain, improves range of motion, decreases muscle stiffness, and allows for improved use of upper extremities.
One dose of Botox lasts between 12-16 weeks, and has been found to be extremely effective in managing spasticity symptoms. This dose is injected into areas needing pain relief in the upper limb muscles.
Botox for Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is a condition that causes excessive sweating that goes beyond the body’s necessity to regulate temperature. This can be a very embarrassing and uncomfortable condition that can significantly interfere with daily activities. Hyperhidrosis often occurs in specific locations, such as under the arms or on the palms. In some cases, it can also be more generalized around the entire body.
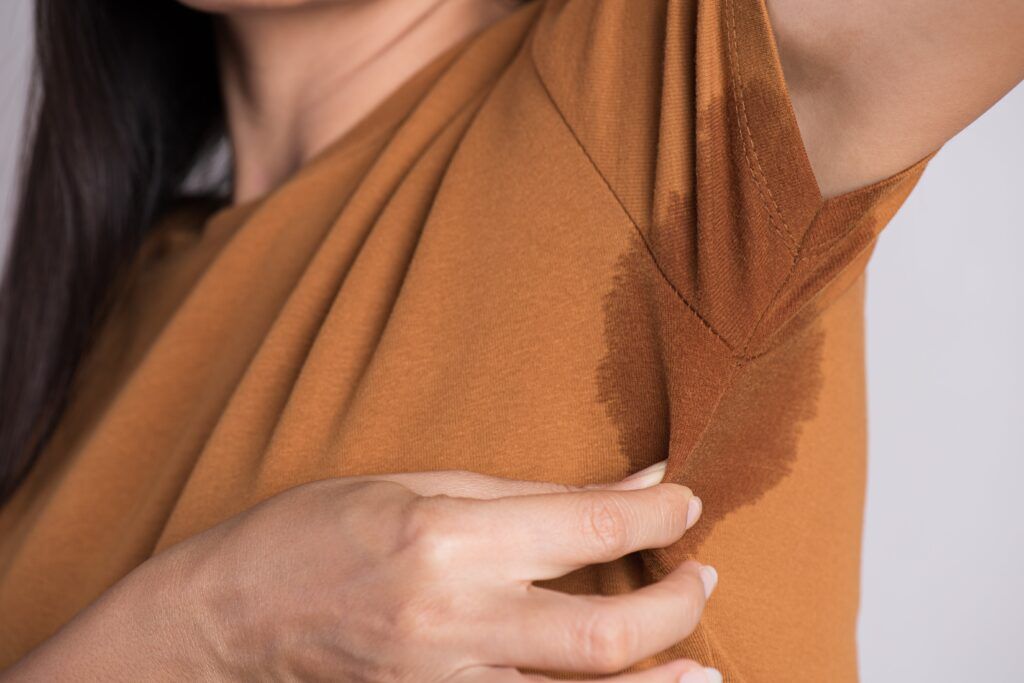

Botox can be used to treat hyperhidrosis by temporarily preventing the nerves responsible for telling the sweat glands to produce sweat. In doing so, this helps reduce sweating. Botox is most commonly injected into the underarms, since it is most effective in this location. In some cases, Botox may also be injected into the feet or palms to treat excessive sweating in these locations.
One Botox treatment can last for around four to six months, at which point retreatment is generally needed. When receiving Botox for hyperhidrosis, you can expect to receive multiple injections. The total number of injections will depend on the size and location of the treatment area. After Botox, patients should notice a significant reduction in their sweating within two weeks.
Botox for Dystonia
Dystonia is a condition that causes involuntary muscle contractions and spasms. This can result in abnormal posture and movements, tremors, and pain. There are many different types of dystonia, each with their own set of symptoms that affect a particular area of the body.
Botox can be used to treat dystonia by relaxing the muscles that are causing the spasms. This can help to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve range of motion. Botox can also be used to prevent dystonia from getting worse. For new Botox patients, a low dose is often used to prevent the risk of adverse reactions such as upper respiratory infections, neck pain, headaches, and dysphagia.
One dose of Botox can last for 2-6 months, and multiple treatments have been found to be effective in managing dystonia symptoms. The injection is usually given in the affected muscles and only takes about 15-25 minutes. Many patients notice an improvement in their symptoms within 2-3 days, which is a major improvement around the four week mark.
Botox for Sialorrhea
Sialorrhea is a condition that causes excessive drooling. Oftentimes sialorrhea is the result of a neurological disorder that impairs the facial muscles such as: Parkinson’s disease, Multiple Sclerosis, ALS, and epilepsy. This can be a very embarrassing and uncomfortable condition.

Botox can be used to treat sialorrhea by temporarily paralyzing the muscles responsible for producing saliva. In doing so, this helps reduce drooling. Studies show that Botox is almost always effective at managing sialorrhea. While it cannot cure the condition, Botox does significantly reduce symptoms.
One Botox treatment can last for around three to four months, at which point retreatment is generally needed. When receiving Botox for sialorrhea, you can expect to receive multiple injections. The total number of injections will depend on the severity of your symptoms. After Botox, patients should notice a significant reduction in their drooling.
In Conclusion
In this blog post, we discussed five ways your neurologist may use Botox: to treat migraines, spasticity, blepharospasm, dystonia, and hyperhidrosis. We explained how each condition can be helped by Botox injections and what you can expect from treatment. If you or someone you know suffers from any of these conditions, consider talking to your neurologist about the possibility of using Botox as a treatment option.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.