Did you know that Botox injections can be used for the treatment of neurological disorders? While many people associate Botox with minimizing facial wrinkles and fine lines, Botox actually has several different applications. In fact, Botox injections are one of the main advancements of managing spasticity and movement disorders.
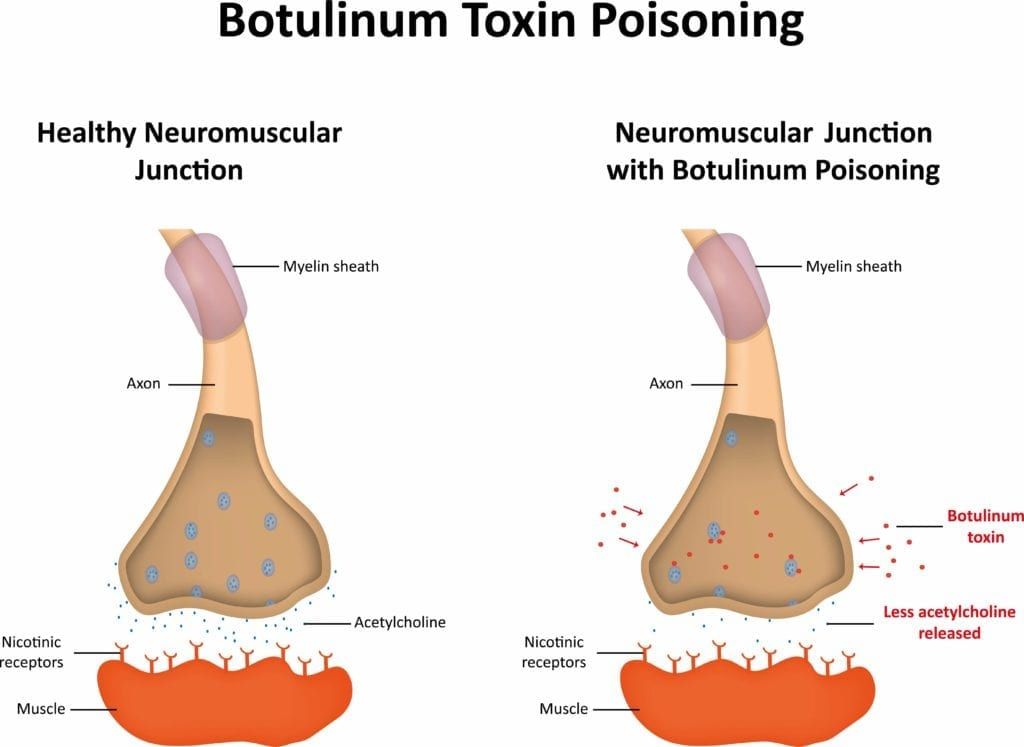
To understand why Botox is beneficial for the treatment of movement disorders, we must first look at the basics of what Botox is and how it affects the body. Botox is a neurotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum bacteria. There are seven distinct variations of this neurotoxin labeled as A-G. Currently only type A (BTX-A) and sometimes type B are being used for regular treatment.
Since BTX-A is a neurotoxin, it blocks neuromuscular transmission when injected into a specific muscle. This results in local paralysis of the affected muscle or group of muscles. This makes it an ideal treatment option for managing focal dystonia and spasticity.
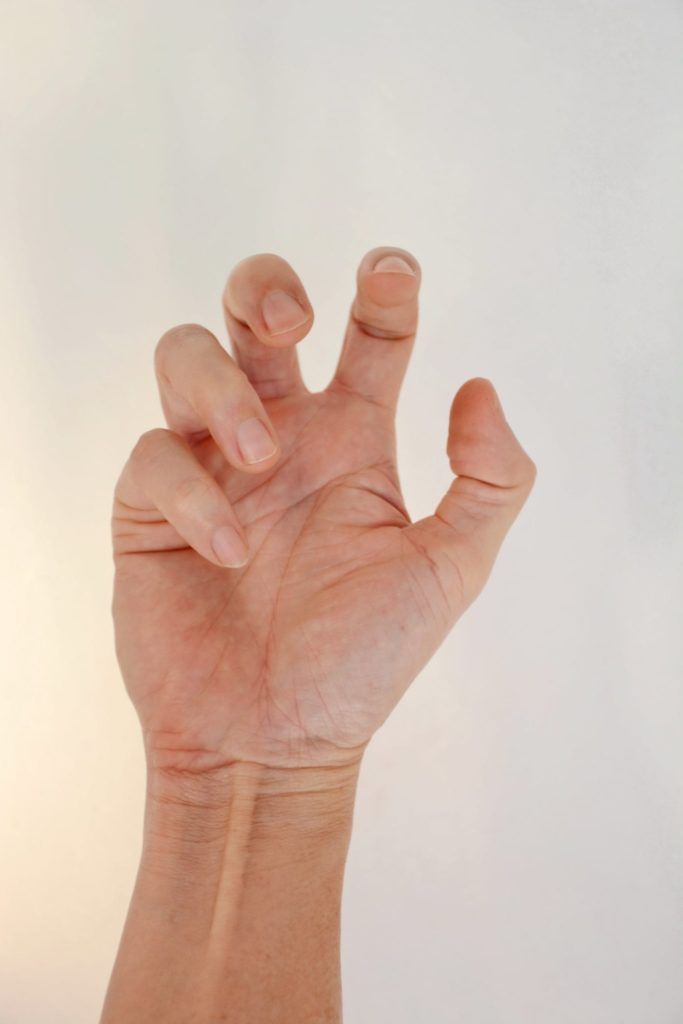
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder that is characterized by twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures caused by sustained or repetitive muscle contractions. It occurs as a result of the brain signaling increased muscle activity.
When BTX-A is used to treat dystonia, it is injected into the muscles displaying increased activity. The neurotoxin interrupts the signal that the brain passes to through the nerves to stimulate muscle movement. The result is reduced muscle spasm. Unfortunately, however, new neurons are eventually developed by the body to restore communication between the brain and muscles. At this point, an immunity to the neurotoxin is developed rendering the treatment ineffective. In these cases, a different brand of the toxin may be used.
Spasticity is a neurological movement disorder that is characterized by muscle stiffness or tightness that inhibits normal, fluid movement. It affects patients with cerebral palsy, as well as some individuals who have suffered a stroke. Although they are similar, dystonia is attributed to an inability to relax the muscles, while spasticity is caused by an hyperactive response to stretching the muscles.
In most cases, spasticity tends to localize to a specific location. This makes it difficult to treat via systematic means. However, BTX-A can be injected into a specific area to alleviate overly active muscle activity. This generally results in a decrease in spasticity and an increase in function.
However, it is important to note that BTX-A is rarely an individual treatment and generally used in coordination with other treatments. In fact, research has suggested that the use of adjunctive therapies generally produces better treatment outcomes. Because of this, BTX-A is often used in coordination with physiotherapy, orthoses, and/or oral medication.
Additionally, it is important to note that BTX-A injections generally do not completely eliminate symptoms in most people. Instead, the injection is expected to significantly relieve symptoms so that they are less severe. After the injection, patients can expect to notice results within 4-7 days. These results generally last for about 12 weeks, but can last up to 16 weeks.
Overall, Botox injections can be used to reduce symptoms associated with dystonia and spasticity by interrupting the brain’s signal for hyperactivity. This makes it an ideal treatment for focal dystonia and spasticity, in addition to physiotherapy, orthoses, and oral medications. If you or someone you love is affected by dystonia or spasticity, schedule a consultation with your local neurologist to discuss how Botox injections can help.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.




