Migraines are more than just headaches—they are complex neurological conditions that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While various treatment options exist, the science of using Botox as a therapy for migraines has gained considerable attention in recent years. Beyond its well-known cosmetic applications, Botox, or botulinum toxin, has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in alleviating the frequency and severity of migraines. By exploring the scientific mechanisms behind Botox as a migraine treatment, we can uncover how this seemingly unconventional approach works and why it holds promise for those seeking relief from the debilitating grip of chronic migraines.
Understanding Migraines:
Before we explore the role of Botox in migraine treatment, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of migraines themselves. Migraines are a type of neurological disorder characterized by recurrent and intense headaches that can be disabling. They are typically pulsating or throbbing in nature and often affect one side of the head. Migraines are usually accompanied by other symptoms such as sensitivity to light, sound, and smells, as well as nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances like flashing lights or blind spots.
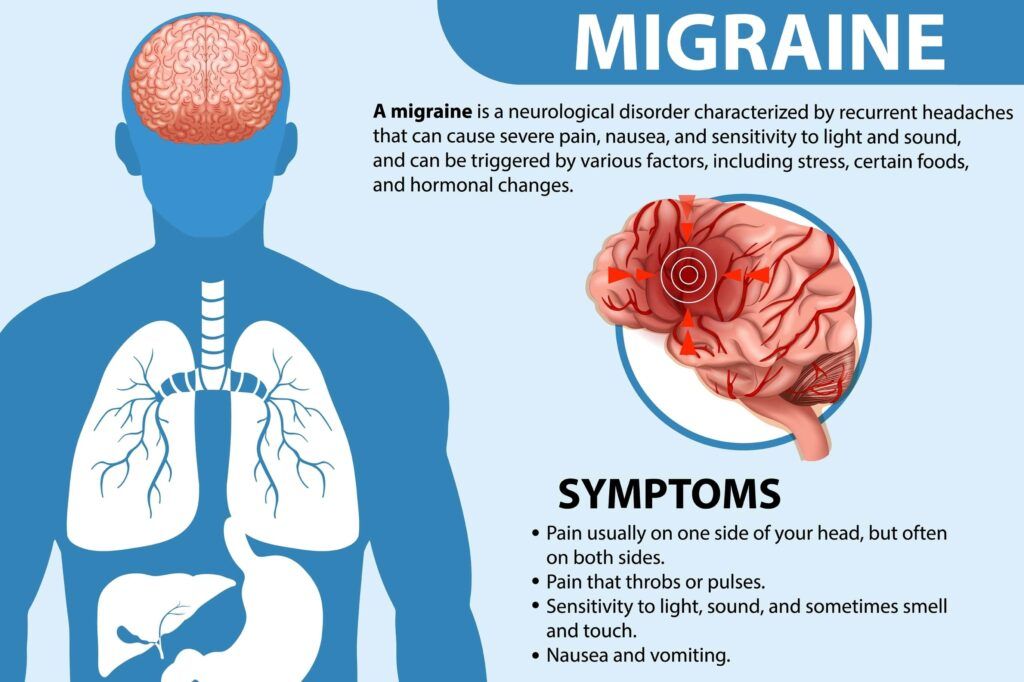
Migraines are more than just severe headaches; they are a complex condition that can significantly disrupt daily life. The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but they are believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Triggers such as certain foods, hormonal changes, stress, sleep disturbances, and sensory stimuli can contribute to the onset of migraines.
The duration and frequency of migraines can vary widely among individuals. Some people experience migraines occasionally, while others may have chronic migraines that occur more frequently. Migraines can last for hours to days and can be accompanied by significant pain and discomfort, making it challenging to carry out regular activities.
It’s important to note that migraines are a distinct neurological disorder and should not be confused with tension headaches or other types of headaches. If you suspect you are experiencing migraines, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies.
Introduction to Botox:
Botox, short for botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxic protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It functions by temporarily paralyzing or weakening specific muscles or blocking nerve signals. Botox works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells and muscles. By interfering with this process, Botox prevents muscle contractions and reduces muscle activity in the targeted area. In cosmetic procedures, Botox is commonly used to temporarily smooth out facial wrinkles and fine lines by relaxing the underlying muscles responsible for their formation. However, Botox also has therapeutic applications in treating various medical conditions, including migraines.
How Botox Works in Migraine Treatment:
Botox works for migraine treatment by targeting specific neurological mechanisms associated with the condition. While the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, several theories have been proposed to explain how Botox can provide relief for migraines.
One theory suggests that migraines may involve hyperexcitability of sensory nerves and the release of certain neurotransmitters, such as substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), which play a role in pain signaling. Botox works by inhibiting the release of these neurotransmitters, thus interrupting the pain pathways and reducing the intensity and frequency of migraines.
Another possible mechanism involves the effect of Botox on muscle tension and relaxation. It is believed that excessive muscle tension in areas such as the forehead, temples, and neck can contribute to migraines. Botox injections into these muscles can help relax them, reducing muscle spasms and alleviating associated pain.
The Process of Administering Botox for Migraines:
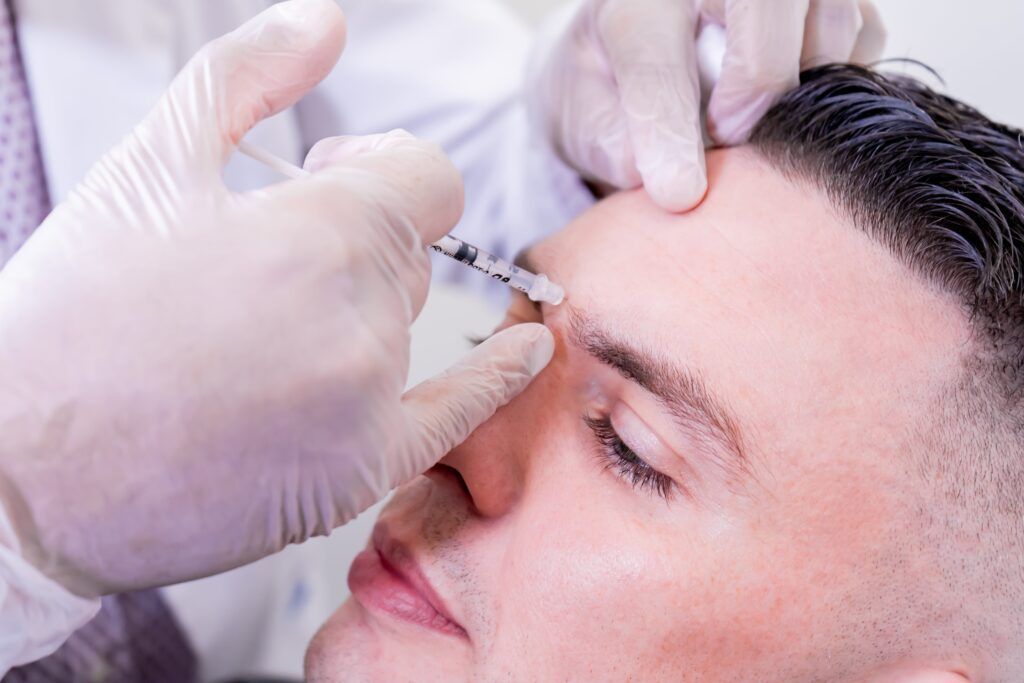
Administering Botox for migraine treatment involves a careful and precise injection technique. During a medical evaluation, healthcare professionals determine whether a patient is suitable for Botox therapy based on specific criteria. The precise administration of Botox for migraines involves a series of injections strategically placed in specific muscles and nerve endings. The treatment typically targets multiple sites based on the individual’s symptoms and patterns of migraine occurrence. The injections are performed by a healthcare professional and require precision to ensure optimal results.
It’s important to note that Botox for migraines is typically used as a preventive treatment rather than an acute pain reliever. The effects of Botox may take time to develop, with improvements gradually occurring over several weeks following treatment. The treatment regimen usually involves repeated sessions every few months to maintain its effectiveness.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in administering Botox for migraines to determine if you are a suitable candidate for this treatment. They will evaluate your medical history, migraine patterns, and overall health to determine if Botox is an appropriate option for managing your migraines effectively.
Effectiveness and Long-Term Benefits of Botox for Migraines:
Scientific studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Botox in reducing migraine frequency and severity. Many individuals who have undergone Botox therapy for migraines report significant improvements in their symptoms, leading to enhanced quality of life. The duration of effect varies from person to person, but many experience relief for several months between treatments. Botox can be a valuable long-term management strategy for chronic migraine sufferers.
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions:
Despite its proven efficacy, some concerns and misconceptions surround Botox as a migraine therapy. It’s important to address these issues to provide clarity and alleviate any apprehensions. Safety is a common concern, but when administered by trained healthcare professionals, Botox for migraines is generally considered safe and well-tolerated.
While Botox is generally well-tolerated when used appropriately, it may have potential side effects and risks. Common side effects include temporary bruising, pain at the injection site, headache, and flu-like symptoms. Serious complications are rare but can occur if Botox spreads beyond the intended area or if there are underlying medical contraindications.
In Conclusion:
The science behind Botox as a migraine therapy offers hope to those who struggle with chronic migraines. By understanding the neurological mechanisms involved and the precise administration of Botox injections, individuals can make informed decisions about their migraine treatment options. Consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial for personalized advice and to explore whether Botox therapy is a suitable choice for managing migraines effectively. With ongoing research and advancements, Botox continues to provide relief and improve the lives of migraine sufferers worldwide.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.




