Muscle spasticity, a common symptom in neurological conditions like Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Muscular Dystrophy, and various other disorders, can be debilitating and adversely affect an individual’s quality of life. Traditional treatments often come with side effects and limited effectiveness. In recent years, medical marijuana has emerged as a promising alternative for managing muscle spasticity. This blog explores the potential benefits of medical marijuana in alleviating muscle spasticity in neurological conditions and sheds light on its growing acceptance in the medical community.
Understanding Muscle Spasticity
Muscle spasticity is a medical condition characterized by abnormal muscle stiffness, tightness, and involuntary muscle contractions or spasms. It occurs when there is a disruption in the communication between the brain and the muscles, often due to damage or dysfunction in the nervous system. This disruption can result from various neurological conditions or injuries.
Key characteristics of muscle spasticity include:
Increased Muscle Tone:
Individuals with muscle spasticity often experience heightened muscle tone, which means their muscles are in a state of continuous contraction. This can lead to stiffness and rigidity in the affected muscles.
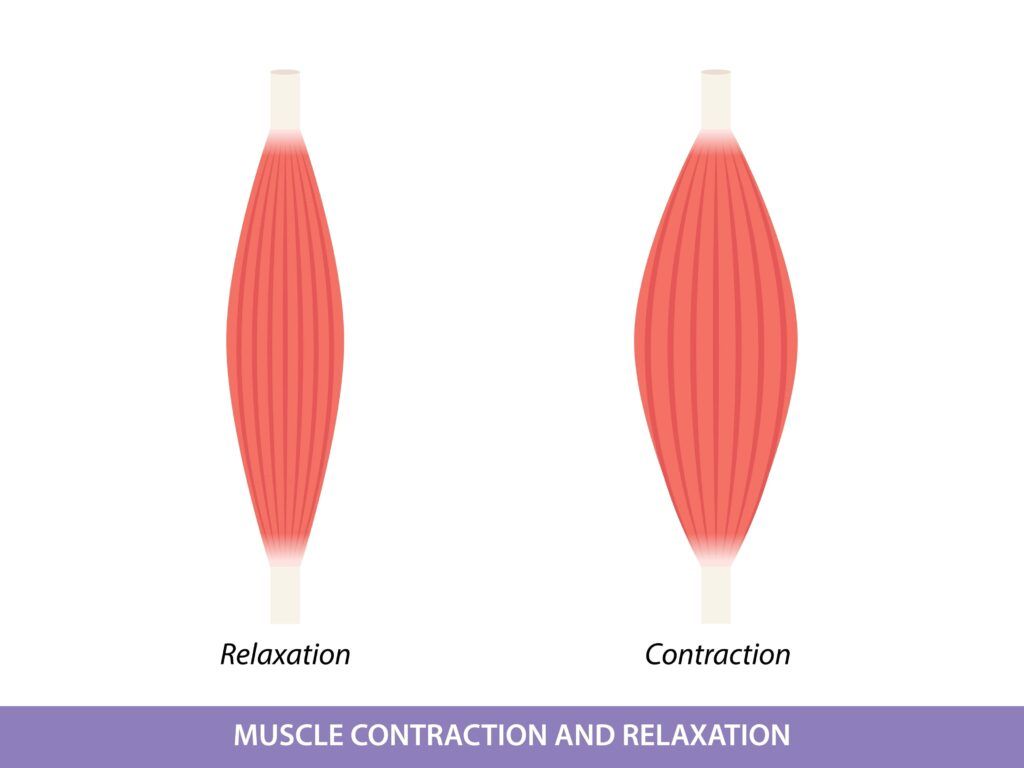
Involuntary Muscle Contractions:
Muscle spasticity causes muscles to contract involuntarily, leading to spasms or jerking movements. These contractions can be sudden and unpredictable.
Resistance to Stretching:
Muscles affected by spasticity resist being stretched or moved, making it challenging to perform everyday activities and causing discomfort.
Reduced Range of Motion:
Due to the increased muscle tone and stiffness, individuals with spasticity may have a limited range of motion in their joints. This can affect mobility and make tasks like walking, reaching, and grasping difficult.
Pain and Discomfort:
Muscle spasticity often leads to pain and discomfort, as the continuous muscle contractions can strain the affected muscles and put additional stress on joints and ligaments.
Muscle spasticity is commonly associated with neurological conditions such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy, Stroke, Spinal Cord Injury, and certain types of brain injuries. It can significantly impact a person’s quality of life by interfering with their ability to move, perform daily activities, and even affect their overall well-being.
The Conventional Approach
The conventional approach to treating muscle spasticity typically involves a combination of therapies and interventions aimed at reducing muscle stiffness, alleviating pain, and improving the individual’s functional abilities. The specific treatments chosen depend on the underlying cause of the spasticity and the severity of the condition. Here are some conventional treatment options:
Oral Medications:
Muscle relaxant medications are often prescribed to reduce muscle spasticity. These medications can include drugs like baclofen, tizanidine, diazepam, and dantrolene. They work by targeting the nervous system to relax muscles and reduce the intensity of spasms.
Botulinum Toxin Injections:
Botulinum toxin injections (commonly known as Botox) can be administered directly into the affected muscles to temporarily paralyze them. This helps reduce muscle spasticity and can provide relief for several months. Repeat injections are typically needed.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing muscle spasticity. Therapists use techniques such as stretching exercises, range of motion exercises, and functional training to improve muscle flexibility and function. Assistive devices like braces and splints may also be recommended.
Occupational Therapy:
Occupational therapists can teach individuals with muscle spasticity strategies for performing daily tasks more efficiently and with less strain. They may suggest adaptive equipment or modifications to the home or work environment.
Orthopedic Surgery:
In severe cases of muscle spasticity that lead to joint deformities or contractures, orthopedic surgeries may be considered. These procedures aim to correct structural abnormalities and improve joint function.
Intrathecal Baclofen Therapy:
For individuals with severe spasticity that does not respond well to oral medications, an implantable pump that delivers baclofen directly to the spinal cord can be considered. This therapy requires surgical implantation.
Nerve Blocks:
In some cases, nerve blocks, which involve injecting anesthetic or medications around specific nerves, may be used to temporarily block nerve signals responsible for muscle spasticity.
Counseling and Psychological Support:
Coping with muscle spasticity can be emotionally challenging. Counseling and support from mental health professionals can help individuals manage the psychological impact of the condition.
Assistive Devices:
The use of assistive devices such as braces, splints, or orthotic devices can provide support, improve mobility, and reduce the impact of muscle spasticity on daily life.
It’s important to note that the choice of treatment varies based on the individual’s unique circumstances and the underlying cause of their muscle spasticity. Additionally, treatment plans may evolve over time as the condition changes or as new therapies become available. Effective management of muscle spasticity often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare providers, therapists, and specialists to provide comprehensive care and support to individuals living with this condition.
Medical Marijuana and Muscle Spasticity
Medical marijuana, also known as medical cannabis, has shown promise in alleviating muscle spasticity in various neurological conditions. Its effectiveness can be attributed to its interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors and molecules in the body that plays a role in regulating various physiological processes, including muscle function and pain perception. Here’s how medical marijuana works for muscle spasticity:
Muscle Relaxation:
Medical marijuana contains compounds known as cannabinoids, with the most well-known being tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). THC has muscle-relaxing properties, and when it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system, it can reduce muscle spasticity. This leads to a relaxation of the affected muscles and a decrease in the severity and frequency of muscle spasms.

Pain Relief:
Both THC and another prominent cannabinoid called cannabidiol (CBD) have analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. Muscle spasticity often comes with pain as a common symptom, and medical marijuana can help mitigate this discomfort by reducing the perception of pain.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
CBD, in particular, has anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammatory processes can contribute to muscle spasticity and pain in neurological conditions. By reducing inflammation in the muscles and nerves, CBD may help decrease spasticity and improve overall comfort.
Improved Sleep:
Many individuals with neurological conditions and muscle spasticity also suffer from disrupted sleep patterns. Medical marijuana, especially strains with higher CBD content, can promote better sleep, which is essential for overall recovery and comfort.
Neuroprotective Effects:
Some research suggests that cannabinoids may have neuroprotective properties, which could be beneficial in preserving nerve function and potentially slowing down the progression of certain neurological conditions.
It’s worth noting that the effectiveness of medical marijuana for muscle spasticity can vary from person to person, and the specific strains and dosages used may need to be tailored to individual needs. Additionally, the choice of marijuana products (e.g., smoked, vaporized, edible, or oil-based) can also impact the onset and duration of its effects.
Research and Evidence
Several studies and anecdotal reports suggest that medical marijuana can be effective in reducing muscle spasticity. For instance, a study published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal found that smoked cannabis significantly reduced muscle spasticity and improved mobility in individuals with MS.
Additionally, the National Multiple Sclerosis Society recognizes the potential benefits of medical marijuana in managing MS-related symptoms, including spasticity, based on the available evidence. They also have provided a link to current research focusing on medical marijuana and MS-related symptoms. With that being said, however, there is still more research to be done in this area to fully understand the relationship between medical marijuana and reducing muscle spasticity.
Consulting with a Medical Marijuana Provider
Before exploring medical marijuana as a treatment option for muscle spasticity, individuals should consult with their healthcare provider. Medical professionals can provide guidance on dosage, potential risks, and monitor the individual’s progress.
Additionally, the legal status of medical marijuana varies from country to country and even within states or regions. It is essential for individuals considering medical marijuana for muscle spasticity to consult with their healthcare providers and adhere to local laws and regulations.
Conclusion
Muscle spasticity can significantly impact the lives of individuals with neurological conditions like MS, Muscular Dystrophy, and more. While conventional treatments have limitations, medical marijuana has shown promise in alleviating muscle spasticity, reducing pain, and improving overall quality of life. As research continues to advance, medical marijuana’s role in managing neurological conditions may become increasingly prominent, offering hope to those in search of effective and alternative solutions. However, it’s essential to approach this treatment option with caution, under the guidance of a board-certified medical marijuana doctor, and in compliance with local laws and regulations.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.




