Medical marijuana has been shown to provide relief for a wide range of medical conditions, including chronic pain, epilepsy, and anxiety. But what exactly is it about this plant that makes it so effective? The answer lies in the endocannabinoid system. In this blog, we will take a closer look at the endocannabinoid system, how it works, and how medical marijuana affects this system to provide potential health benefits.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes and maintaining homeostasis (balance) in the body. The endocannabinoid system is composed of three main components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
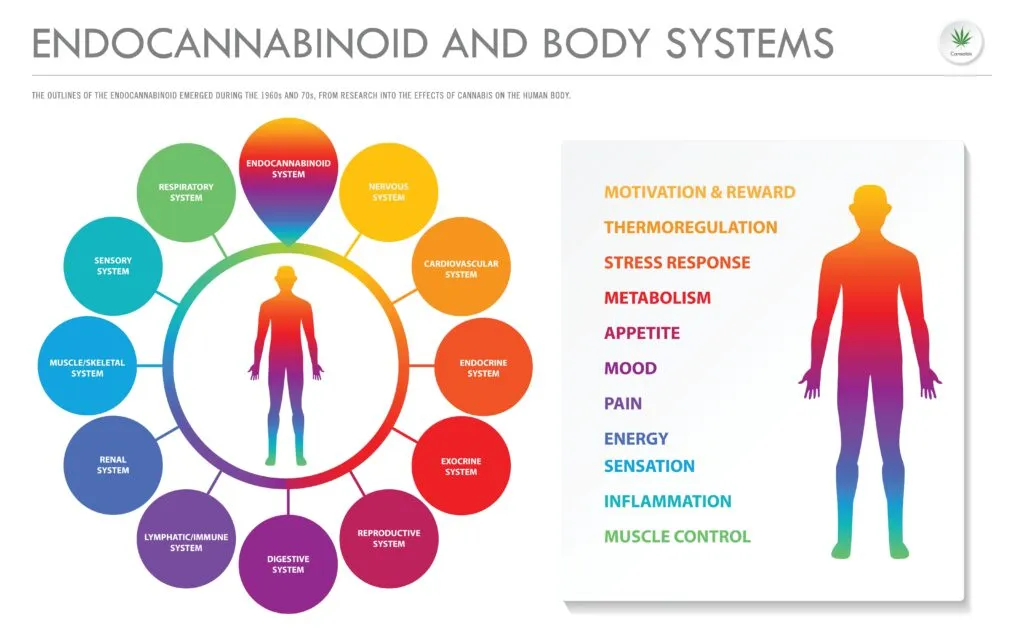
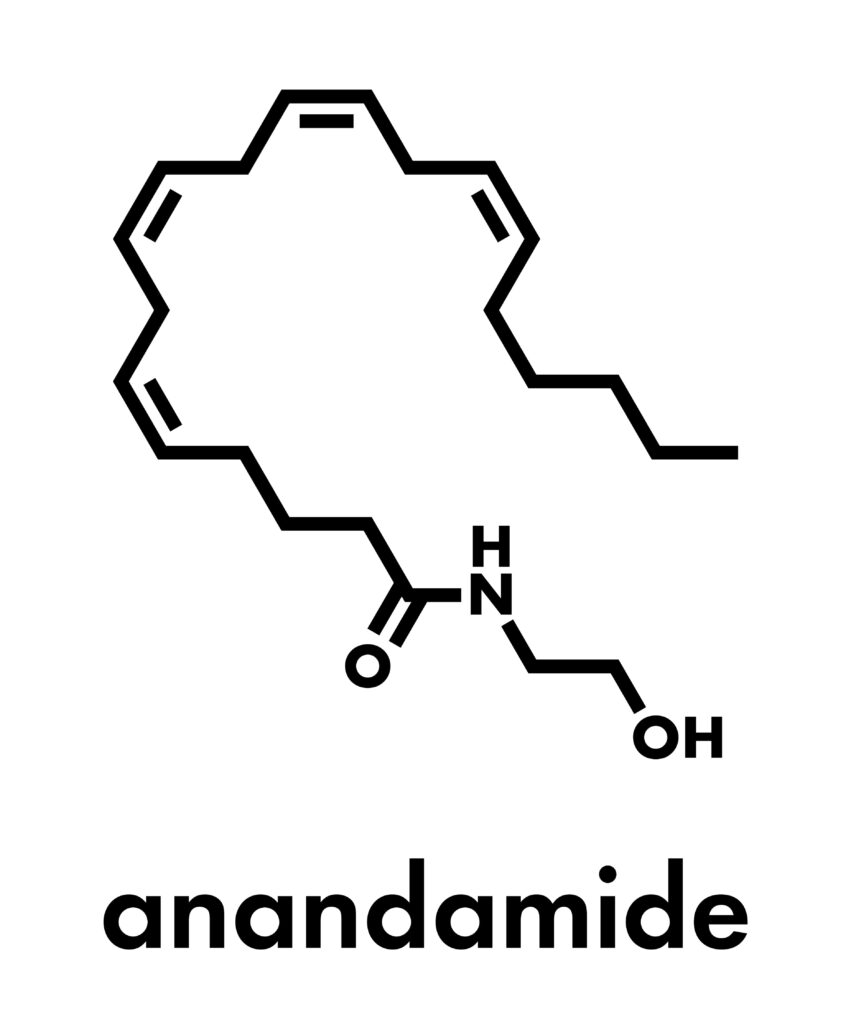
- Endocannabinoids: These are endogenous (meaning naturally occurring within the body) lipid-based neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors. The two main types of endocannabinoids are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
- Receptors: Cannabinoid receptors are found throughout the body and are divided into two main types: CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system (including the brain), and CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in peripheral tissues and cells of the immune system. These receptors are responsible for receiving and transmitting signals to regulate physiological processes in the body.
- Enzymes: Enzymes play a crucial role in the ECS by breaking down endocannabinoids after they have fulfilled their functions. The two main enzymes involved in the ECS are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), which breaks down 2-AG.
Together, these three components work to regulate various physiological processes in the body, such as mood, appetite, sleep, pain, inflammation, and immune function, to maintain homeostasis. Dysregulation within the ECS has been linked to several medical conditions, such as anxiety, depression, chronic pain, and epilepsy.
How Does Medical Marijuana Affect the Endocannabinoid System?
Medical marijuana contains two primary compounds: THC and CBD. THC is the compound responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana use, while CBD is non-psychoactive and has been shown to have a range of potential health benefits. Both THC and CBD interact with the endocannabinoid system in different ways.
THC and the Endocannabinoid System
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system by binding to CB1 receptors, which are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system.
When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it can activate a range of cellular responses that affect various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, and pain perception. This can result in the characteristic psychoactive effects associated with cannabis use, such as feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception.
In addition to its effects on CB1 receptors, THC can also indirectly affect the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting the enzymes responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids like anandamide. This can lead to an increase in the levels of endocannabinoids in the body, which may contribute to some of the potential therapeutic effects of THC.
It’s important to note that while THC has the potential to provide a range of potential health benefits, its psychoactive effects and potential for abuse have led to some controversy and legal restrictions on its use. Additionally, the effects of THC on the endocannabinoid system can vary depending on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, and individual differences in genetics and physiology.
CBD and the Endocannabinoid System
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant that has been the subject of growing interest for its potential therapeutic properties. CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system in a more indirect way compared to THC.
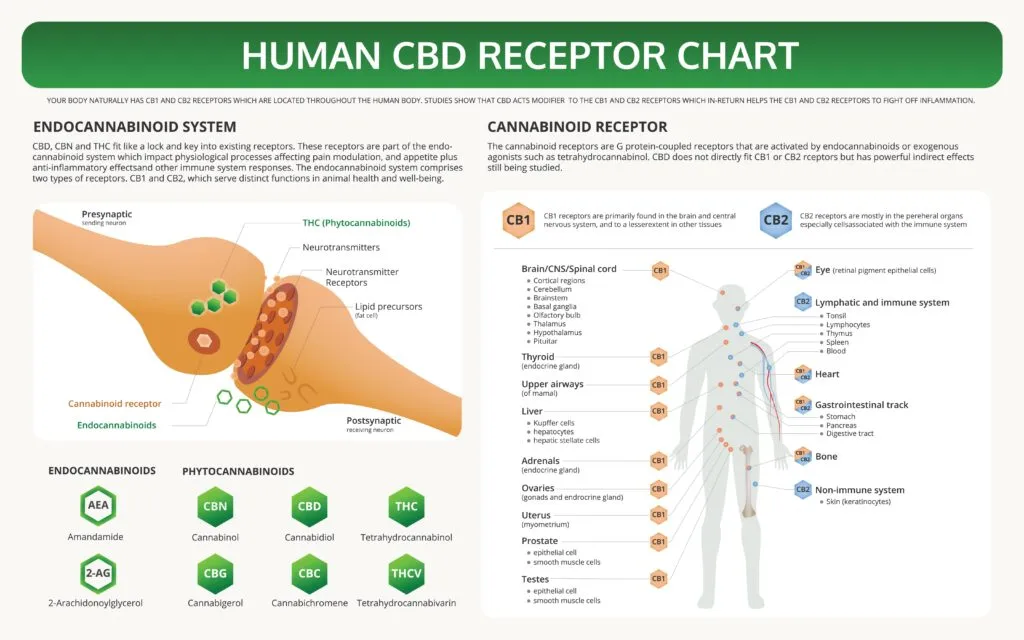
CBD does not directly bind to cannabinoid receptors, but it can interact with them in a more subtle way. Instead, CBD interacts with other receptors, including serotonin and TRPV1 receptors, which are involved in regulating mood, pain perception, and inflammation. CBD can also indirectly affect the endocannabinoid system by increasing levels of anandamide, a naturally occurring endocannabinoid, by inhibiting its breakdown through the enzyme FAAH.
CBD also interacts with a variety of other receptors and ion channels in the body, which may contribute to its potential therapeutic effects. For example, CBD has been shown to interact with the 5-HT1A receptor, which is involved in regulating serotonin levels and has been linked to anxiety and depression.
While research is still ongoing, CBD has shown promise in a range of potential therapeutic applications, including pain management, anxiety and depression, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. However, it’s important to note that the effects of CBD can vary depending on factors such as dosage, frequency of use, and individual differences in genetics and physiology.
The Entourage Effect
One theory that helps explain the effectiveness of medical marijuana is the entourage effect. The entourage effect refers to the synergistic interactions between the various compounds found in the cannabis plant, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. These compounds work together to enhance each other’s potential therapeutic effects, resulting in a more potent and beneficial overall effect than any individual compound could produce on its own.
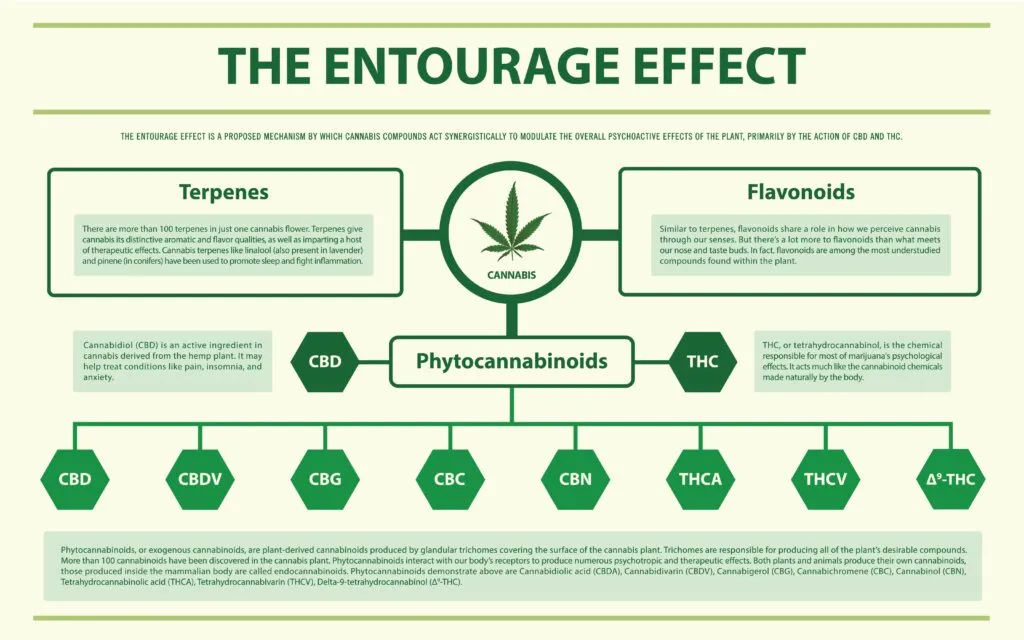
For example, THC and CBD are two of the most well-known cannabinoids found in cannabis. While both compounds have potential therapeutic benefits on their own, studies have suggested that they may work together in a synergistic way to produce even greater therapeutic effects. In addition, terpenes, which are aromatic compounds found in the cannabis plant and other plants, can also interact with cannabinoids to enhance their effects.
The entourage effect is thought to play a crucial role in the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabis, particularly in whole-plant extracts that contain a variety of compounds. Some studies have suggested that isolating individual compounds from the plant may not be as effective as using the whole plant extract, which contains a range of compounds that work together in a synergistic way.
However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind the entourage effect and how it can be optimized for therapeutic purposes.
Endocannabinoid Deficiency
Another theory that helps explain the effectiveness of medical marijuana is endocannabinoid deficiency. Endocannabinoid deficiency is a theoretical condition in which the body’s endocannabinoid system is not functioning properly, leading to a range of potential health issues. Some researchers have proposed that this condition may contribute to a variety of medical conditions, including migraines, irritable bowel syndrome, and other chronic pain conditions.
The idea behind endocannabinoid deficiency is that the body may not be producing or utilizing enough endocannabinoids to properly regulate various physiological processes. This can lead to imbalances in the body that may contribute to the development or exacerbation of certain medical conditions.
One potential implication of endocannabinoid deficiency is that medical marijuana may be particularly effective in treating conditions related to this condition. The cannabinoids found in cannabis, such as THC and CBD, can interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and potentially help to restore balance to various physiological processes. This may be particularly important in conditions where the endocannabinoid system is not functioning properly, as medical marijuana may be able to supplement or replace the body’s own endocannabinoids.
While the idea of endocannabinoid deficiency is still a matter of debate and ongoing research, it highlights the potential importance of the endocannabinoid system in maintaining overall health and wellness. Further research is needed to fully understand the role of the endocannabinoid system in various medical conditions and how medical marijuana may be able to effectively address these conditions.
In Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system plays a vital role in maintaining balance within the body, and medical marijuana has been shown to interact with this system in a number of ways to provide potential health benefits. By understanding the endocannabinoid system and how it interacts with medical marijuana, we can better understand the potential benefits of this plant and how it may be used to treat a wide range of medical conditions. For more information about how medical marijuana can help you, schedule a consultation with one of our board-certified medical marijuana doctors at Premier Neurology in Stuart, FL.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.





