In recent years, the use of synthetic cannabinoids has garnered significant attention in the field of neurological care. These lab-created compounds, designed to mimic the effects of naturally occurring cannabinoids found in cannabis, have shown promise in managing a variety of neurological conditions. From providing relief for chronic pain to aiding in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, synthetic cannabinoids offer a range of potential benefits. However, like any medical treatment, they come with their own set of risks and challenges. In this blog, we will delve into the pros and cons of synthetic cannabinoids, exploring their applications, benefits, and drawbacks, and providing a balanced perspective on their role in modern neurological care.
In This Blog:
- Understanding Synthetic Cannabinoids
- Applications in Neurological Care
- Pros of Synthetic Cannabinoids
- Cons of Synthetic Cannabinoids
- Comparison with Natural Cannabinoids
Understanding Synthetic Cannabinoids
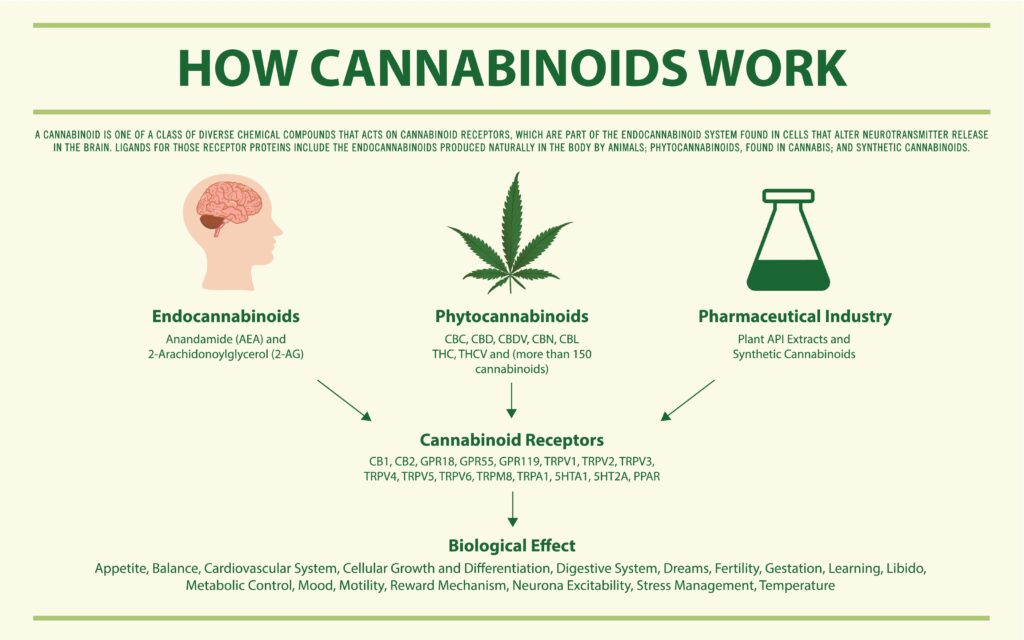
Synthetic cannabinoids are a class of compounds designed to interact with the same cannabinoid receptors in the brain and body as natural cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, found in the cannabis plant. These synthetic compounds are typically created in laboratories and can vary widely in their chemical structure and potency.

One of the key distinctions between natural and synthetic cannabinoids is their origin. While natural cannabinoids are derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, synthetic cannabinoids are man-made and often have a different chemical composition. Despite these differences, both types of cannabinoids aim to achieve similar therapeutic effects by binding to cannabinoid receptors, particularly CB1 and CB2, which are part of the endocannabinoid system.
The mechanism of action of synthetic cannabinoids involves the activation of these receptors, which play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including pain perception, mood, appetite, and memory. By targeting these receptors, synthetic cannabinoids can modulate the release of neurotransmitters and influence neuronal activity, offering potential therapeutic benefits for a range of neurological conditions.
Synthetic cannabinoids are often engineered to provide more targeted and potent effects compared to their natural counterparts. This allows for the development of specific formulations tailored to treat particular symptoms or conditions. However, the potency and efficacy of synthetic cannabinoids can also lead to more pronounced side effects, necessitating careful consideration and monitoring in clinical use.
Understanding the unique properties and mechanisms of synthetic cannabinoids is essential for evaluating their potential in neurological care. In the following sections, we will explore how these compounds are applied in treating various neurological disorders and the pros and cons associated with their use.
Applications in Neurological Care
Synthetic cannabinoids have emerged as a potential therapeutic option for a variety of neurological conditions, offering benefits through their ability to modulate the endocannabinoid system. Here, we explore some of the key applications of synthetic cannabinoids in neurological care:
Pain Management
Chronic pain is a common and debilitating symptom in many neurological disorders. Synthetic cannabinoids have shown promise in providing analgesic effects by interacting with CB1 receptors in the brain and CB2 receptors in the immune system. These interactions can help reduce pain perception and inflammation, making synthetic cannabinoids a valuable option for patients who do not respond well to traditional pain medications.

Neurodegenerative Diseases
Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease involve the progressive degeneration of neurons, leading to cognitive decline and motor dysfunction. Synthetic cannabinoids have been studied for their neuroprotective properties, which may help slow the progression of these diseases. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, synthetic cannabinoids can potentially protect neuronal health and improve quality of life for patients.
Epilepsy and Seizure Control
Synthetic cannabinoids have shown efficacy in reducing the frequency and severity of seizures in patients with epilepsy, including those with treatment-resistant forms of the condition. Compounds like nabilone and dronabinol have been used to control seizures by modulating neuronal excitability and neurotransmitter release, offering an alternative to conventional antiepileptic drugs.
Multiple Sclerosis Symptom Relief
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is characterized by immune-mediated damage to the central nervous system, leading to symptoms such as muscle spasticity, pain, and fatigue. Synthetic cannabinoids can alleviate these symptoms by interacting with the endocannabinoid system to reduce muscle spasticity and pain, improving mobility and comfort for MS patients.
Anxiety and Depression Treatment
Anxiety and depression are common comorbidities in many neurological conditions. Synthetic cannabinoids, by modulating the endocannabinoid system, can influence mood regulation and have anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. These compounds can be particularly beneficial for patients who experience anxiety and depression as a result of their neurological disorder.
In summary, synthetic cannabinoids offer a versatile and potentially effective treatment option for various neurological conditions. Their ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system provides therapeutic benefits ranging from pain relief to neuroprotection and symptom management. However, the use of synthetic cannabinoids must be carefully considered in the context of their potential risks and side effects, which we will explore in the next section.
Pros of Synthetic Cannabinoids
Synthetic cannabinoids offer several potential benefits in neurological care, making them a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal for various conditions. Here are some of the key advantages:
Controlled Dosage and Consistency
One of the primary benefits of synthetic cannabinoids is the ability to deliver precise and consistent dosages. Unlike natural cannabinoids, which can vary in concentration and potency, synthetic cannabinoids are manufactured under strict conditions, ensuring uniformity in their composition. This consistency allows for more accurate dosing and predictable therapeutic effects, which is crucial in managing neurological conditions.
Specific Targeting of Cannabinoid Receptors
Synthetic cannabinoids are designed to specifically target cannabinoid receptors, such as CB1 and CB2, with greater precision. This targeted approach can enhance their therapeutic efficacy, as the compounds can be tailored to interact with particular receptors associated with certain neurological symptoms. For instance, targeting CB1 receptors can help with pain relief, while CB2 receptor activation can modulate immune responses.
Potential for Fewer Side Effects Compared to Traditional Medications
Many traditional medications used in neurological care, such as opioids for pain management or antiepileptic drugs, come with significant side effects and risks. Synthetic cannabinoids can offer a safer alternative for some patients, as they may produce fewer and less severe side effects. Additionally, synthetic cannabinoids can be designed to minimize psychoactive effects, making them more suitable for patients who need to maintain daily functioning.
Customization for Specific Neurological Conditions
The versatility of synthetic cannabinoids allows for the development of specific formulations tailored to different neurological conditions. For example, certain synthetic cannabinoids can be engineered to provide neuroprotective effects for neurodegenerative diseases or anticonvulsant properties for epilepsy. This customization enhances their therapeutic potential and allows for more targeted treatment strategies.
Research-Backed Efficacy in Certain Treatments
There is a growing body of research supporting the efficacy of synthetic cannabinoids in treating various neurological conditions. Clinical studies have demonstrated their effectiveness in reducing seizure frequency in epilepsy, alleviating muscle spasticity in multiple sclerosis, and providing pain relief in chronic pain conditions. This evidence base provides confidence in their therapeutic potential and encourages further exploration and development.
In conclusion, synthetic cannabinoids offer several compelling advantages in neurological care, including controlled dosage, targeted receptor interaction, potential for fewer side effects, customization for specific conditions, and research-backed efficacy. However, it is essential to balance these benefits with the potential risks and challenges associated with their use, which we will discuss in the following section.
Cons of Synthetic Cannabinoids
While synthetic cannabinoids offer several potential benefits, their use in neurological care is not without significant drawbacks. It is crucial to weigh these cons to make informed decisions about their application in clinical practice. Here are some of the key concerns:
Potential for Severe Side Effects
One of the most significant risks associated with synthetic cannabinoids is the potential for severe side effects. These can include psychosis, hallucinations, anxiety, and cardiovascular issues such as increased heart rate and hypertension. The synthetic nature of these compounds can lead to unpredictable reactions, especially when used in higher doses or for extended periods.
Lack of Long-Term Safety Data
The long-term safety of synthetic cannabinoids remains uncertain due to limited research. While short-term studies have shown promise, there is a lack of data on the chronic use of these compounds. Potential long-term effects, including cognitive impairment, addiction, and mental health issues, need further investigation to ensure their safe use in neurological care.
Risk of Addiction and Misuse
Synthetic cannabinoids carry a risk of addiction and misuse, similar to other psychoactive substances. The potency of some synthetic cannabinoids can lead to dependence, with withdrawal symptoms appearing upon cessation. Additionally, the potential for misuse is a significant concern, particularly in populations with a history of substance abuse.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The legal status of synthetic cannabinoids varies widely across different regions, posing challenges for their clinical use. In some areas, synthetic cannabinoids are classified as controlled substances, limiting their availability and hindering research efforts. Navigating the complex legal and regulatory landscape can be a barrier to accessing these treatments for both patients and healthcare providers.
Variability in Patient Response
Patient response to synthetic cannabinoids can be highly variable, making it challenging to predict therapeutic outcomes. Factors such as genetic makeup, existing medical conditions, and concurrent medications can influence how individuals react to synthetic cannabinoids. This variability necessitates a personalized approach to treatment, which can be resource-intensive and complex to manage.
In summary, while synthetic cannabinoids have the potential to offer significant therapeutic benefits in neurological care, they also present several risks and challenges. These include the potential for severe side effects, lack of long-term safety data, risk of addiction and misuse, legal and regulatory hurdles, and variability in patient response. These cons must be carefully considered and addressed to ensure the safe and effective use of synthetic cannabinoids in treating neurological conditions.
Comparison with Natural Cannabinoids
The debate between the use of synthetic and natural cannabinoids in neurological care centers around their efficacy, safety profiles, patient preferences, and regulatory considerations. Here, we compare these two classes of cannabinoids to highlight their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Efficacy and Safety Profiles
- Efficacy: Both synthetic and natural cannabinoids have shown efficacy in treating neurological conditions such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain. However, synthetic cannabinoids can be engineered to target specific receptors more precisely, potentially offering enhanced therapeutic effects for certain conditions. On the other hand, natural cannabinoids like CBD and THC have a broader spectrum of activity, which can be beneficial in managing complex symptoms.
- Safety: Natural cannabinoids, particularly those derived from hemp with low THC content, tend to have a more favorable safety profile with fewer severe side effects. Synthetic cannabinoids, due to their potency and chemical variability, can pose higher risks of adverse effects such as psychosis, cardiovascular issues, and addiction. The long-term safety of synthetic cannabinoids is also less established compared to natural cannabinoids.
Patient Preferences and Accessibility
- Patient Preferences: Many patients prefer natural cannabinoids due to their long history of use, perceived natural benefits, and lower risk of severe side effects. The psychoactive effects of natural THC are also well-documented, allowing patients and healthcare providers to better manage and anticipate its impact.
- Accessibility: Natural cannabinoids, especially those derived from hemp, are more widely available and often legally accessible in many regions. Synthetic cannabinoids, on the other hand, face stricter regulatory controls, which can limit their availability and use. The cost of synthetic cannabinoids can also be higher due to the complexity of their production.
Regulatory Landscape and Availability
- Regulatory Landscape: The legal status of natural cannabinoids varies, but there has been a trend towards greater acceptance and legalization, particularly for medical use. This has facilitated easier access and more research into their benefits and risks. Synthetic cannabinoids often fall under stricter regulatory scrutiny, with many classified as controlled substances, complicating their clinical use and research efforts.
- Availability: Natural cannabinoids are available in various forms, including oils, tinctures, edibles, and inhalable products, offering patients multiple options for administration. Synthetic cannabinoids are typically available through prescription medications, limiting their forms and accessibility.
Research and Evidence Base
- Natural Cannabinoids: There is a growing body of research supporting the therapeutic benefits of natural cannabinoids, particularly CBD and THC, for various neurological conditions. The wealth of anecdotal evidence and patient testimonials further supports their use.
- Synthetic Cannabinoids: While synthetic cannabinoids are supported by rigorous clinical trials demonstrating their efficacy in specific conditions, the overall volume of research is smaller compared to natural cannabinoids. Ongoing studies are crucial to further establish their safety and effectiveness.
In conclusion, both synthetic and natural cannabinoids have their place in neurological care, each with unique advantages and challenges. Synthetic cannabinoids offer precise targeting and potential customization but come with higher risks and regulatory hurdles. Natural cannabinoids are more accessible and have a more established safety profile but may offer less targeted therapeutic effects. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions about the use of cannabinoids in treating neurological conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, synthetic cannabinoids represent a promising yet complex option in the realm of neurological care. Their ability to deliver precise and consistent dosages, target specific cannabinoid receptors, and potentially offer safer alternatives to traditional medications makes them a valuable tool in managing various neurological conditions. However, these benefits must be carefully weighed against significant risks, including severe side effects, lack of long-term safety data, potential for addiction and misuse, and regulatory challenges. When compared to natural cannabinoids, synthetic variants offer tailored therapeutic possibilities but face hurdles in accessibility and patient acceptance. As research continues to evolve, a balanced and informed approach will be essential in integrating synthetic cannabinoids into neurological practice, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and safest treatments available.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.





