Nerves are the wiring in your body that travel down your spinal cord and connect your brain to every part of the body. When functioning properly, nerves are able to communicate different forms of sensory information to the brain. Unfortunately, however, nerves can go wrong in many ways and cause problems like chronic pain or numbness. One of these problems is known as radiculopathy and it can affect the spinal nerves. In this blog, we are going to explain exactly what radiculopathy is, why it occurs, and how a neurologist can help with treatment.
What is radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy is a medical condition that affects the nerves in the spine. The term “radiculopathy” is derived from the Latin words radix (root) and pathos (disease). This means that the roots of the nerves that travel down your spine from the brainstem are affected by trauma, nerve compression, or diabetes or other diseases.
There are different types of radiculopathy, such as:
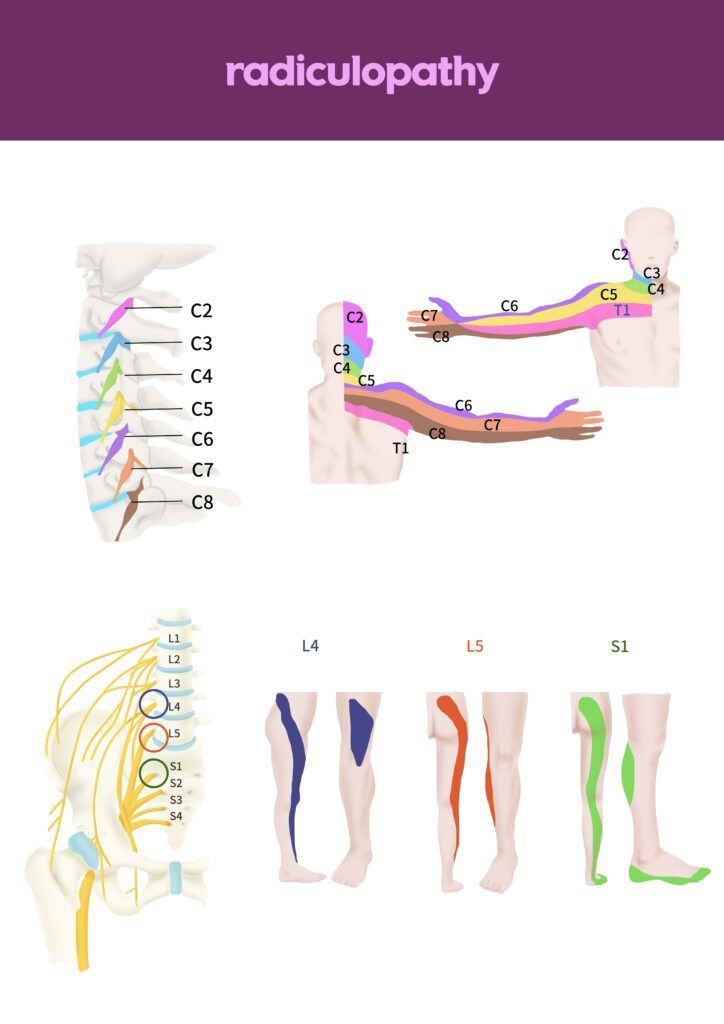
Cervical Radiculopathy
Cervical radiculopathy affects nerve roots in the cervical spine, which is located in the neck. When nerve roots in the cervical spine become inflamed or damaged, this can cause numbness, weakness, or altered reflexes in the neck, shoulder, arm, hand, or fingers. It can also cause tingling or pain that radiates down into the arm and/or hand.
Thoracic Radiculopathy
Thoracic radiculopathy affects nerve roots in the thoracic spine, which is located in the upper back and shoulder area. When nerve roots in the thoracic spine become inflamed or damaged, this can cause numbness, weakness, or pain that radiates to the front of the body. In many cases thoracic radiculopathy can be misdiagnosed as shingles or complications with the heart, abdomen, or gallbladder since this condition is rare.
Lumbar Radiculopathy
Lumbar radiculopathy affects nerve roots in the lumbar spine, which is located in the lower back. When nerve roots in the lumbar spine become inflamed or damaged, this can cause numbness, weakness, or pain that radiates down the back of the leg and/or below. This is commonly known as sciatica and it tends to get worse when sitting or walking for long periods of time. In rare cases, lumbar radiculopathy can also cause bladder or bowel incontinence if these nerves are affected.
What causes radiculopathy?
The cause of most radicular problems is compression of one or more spinal nerves. These nerves come from specific places in your brainstem and spinal cord, making up part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). They travel through the spine either on their own or as part of a larger nerve, like the sciatic nerve. When something is wrong with these nerves, this can cause pain in your back that radiates into other areas such as one leg or an arm. This is because the nerve roots (the part that comes out) can become compressed or irritated, which interrupts your body’s ability to communicate with the brain.
This can be caused by a herniated disc, osteophyte formation on the vertebrae (bone spurs), or narrowing of the spinal canal. This causes irritation and inflammation to the nerve root which can then cause pain, numbness, weakness in your arms or legs, depending on where it is located.
However there are other causes that can include:
- Degenerative disc disease (a condition involving the breakdown of discs which may cause nerve compression)
- Spinal stenosis (narrowing of spaces within your spine that can put pressure on nerves)
- Vascular problems such as diabetes, subclavian steal syndrome or vertebral artery dissection.
How Neurologists Diagnose & Treat Radiculopathy
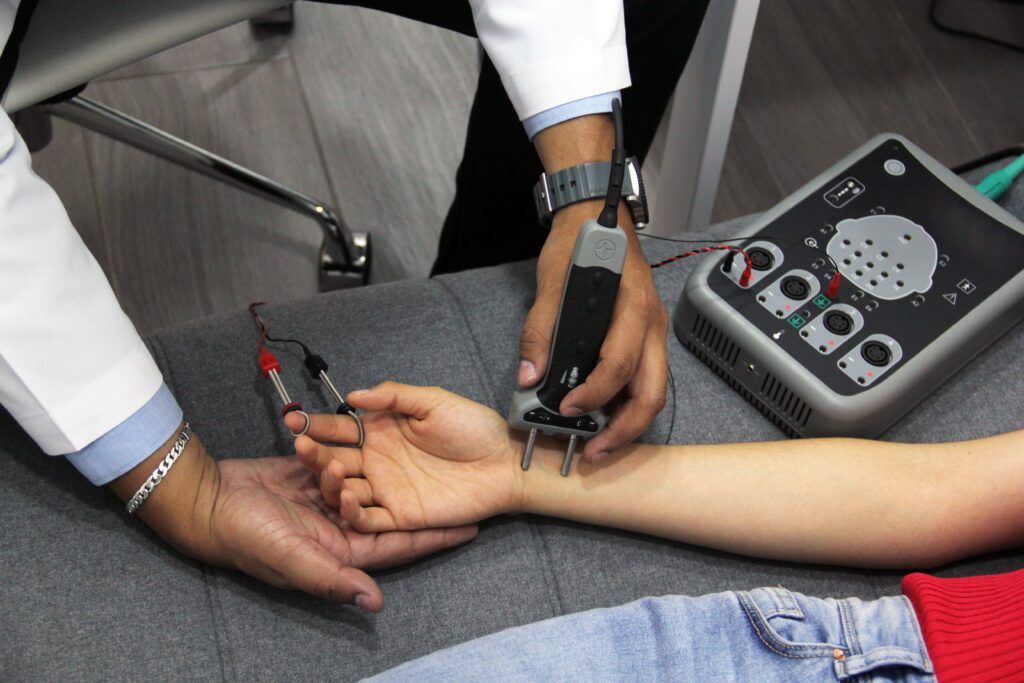
Neurologists use multiple methods to diagnose radiculopathy. Oftentimes, the diagnostic process begins with a discussion of your symptoms, medical history, and current medications. A physical exam will also be performed and additional diagnostic testing may be required if radiculopathy is suspected. A neurologist might observe radiculopathy with an MRI scan and then recommend an electrodiagnostic study (EMG) to distinguish radiculopathy from other conditions. Electrodiagnostic studies use nerve conduction studies (NCS) and needle electromyography (EMG) to evaluate the peripheral nervous system.
During a nerve conduction study, small electrodes are placed on the skin over specific muscles. Electrical signals are transmitted through these electrodes that stimulate your nerves and record how fast or slow nerve impulses travel from one site to another. This test can determine if there is damage to the nerve root in the spinal cord and can pinpoint the location of the damage. The needle electromyography (EMG) study uses a thin electrode inserted into a targeted muscle to record the electrical activity of the muscle fibers. Both tests can provide valuable diagnostic information.
The responsibility of a neurologist is to develop the best possible therapeutic plan for people to regain sensation and relieve pain. Treatment may include physical therapy, medication, surgery, injections into the affected area to provide relief from pain, or spinal cord stimulation.
In Conclusion
If you’re experiencing pain and other symptoms that radiate across the front of your body or down your arms or legs, it may be due to a problem with spinal nerves. A neurologist can diagnose the condition as well as provide treatment options such as injections or physical therapy. If you think you have radiculopathy, contact our team of neurology experts today so we can help develop an actionable plan for reducing your symptoms and increasing your mobility.

Dr. Kashouty, a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology (ABPN), practices general neurology with fellowship trained specialization in clinical neurophysiology. Dr. Kashouty finds the form and function of the nerves and muscles the most interesting part of neurology, which is what led him to specialize in neurophysiology with more emphasis on neuromuscular conditions. He treats all neurological diseases, but his main focus is to treat and manage headaches, movement disorders and neuromuscular diseases.