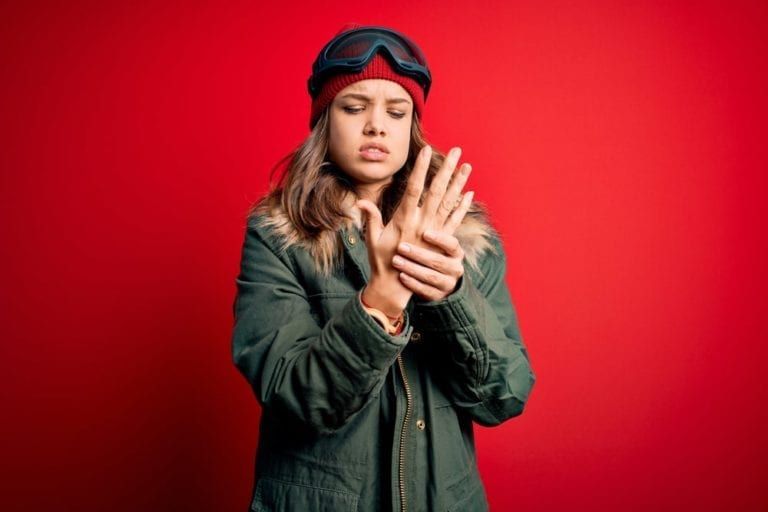
Peripheral Neuropathy: Causes and Management Strategies
Peripheral neuropathy, a common neurological disorder, affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when nerves outside the brain and spinal cord—known as peripheral nerves—are damaged, leading to a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. This condition manifests in numerous forms, including sensory, motor, and autonomic neuropathy, each affecting different nerve functions. The causes of peripheral neuropathy are diverse, ranging from diabetes and autoimmune diseases to genetic factors and environmental exposures. Understanding the nature of this disorder, its diagnostic processes, and the effective management strategies available is essential for those affected. This blog aims to delve into the intricacies of peripheral neuropathy, offering insight into its causes and discussing comprehensive management strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.